Effects of C-reactive Protein and Homocysteine on Cytokine Production: Modulation by Pravastatin
- PMID: 20157364
- PMCID: PMC2817441
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1753-5174.2007.00003.x
Effects of C-reactive Protein and Homocysteine on Cytokine Production: Modulation by Pravastatin
Abstract
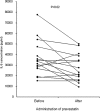
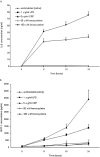
OBJECTIVE: C-reactive protein (CRP) and homocysteine are markers of cardiovascular risk that may have inflammatory effects. HMG coenzyme A reductase inhibitors (statins) have anti-inflammatory effects in vitro, but it is not clear if such responses in vivo are secondary to lipid lowering. We examined the hypothesis that CRP and homocysteine would stimulate cytokine release in human whole blood and that short-term treatment with a statin would inhibit it. METHODS: The time course of IL-6 and MCP-1 production was determined in whole blood incubated with saline, 1 microg/mL lipopolysaccaride (LPS), 50 and 100 microM/L DL-homocysteine, and 5 microg/mL human recombinant CRP for 24 hours at 37 degrees C under 5% CO(2) atmosphere. Cytokine responses were determined in blood drawn from 15 healthy volunteers before and after administration of pravastatin 40 mg daily for 2 days. RESULTS: Both human recombinant CRP and LPS significantly increased the production of IL-6 and MCP-1 in whole blood samples more than 4-fold (P < 0.001) but homocysteine did not. Oral administration of pravastatin, 40mg daily for 2 days, decreased CRP-stimulated IL-6 production by approximately 20% (P = 0.02) 6 hours after incubation, but did not affect MCP-1 production (P = 0.69). Pravastatin treatment did not affect LPS-stimulated MCP-1 but increased IL-6 modestly. CONCLUSIONS: CRP stimulated the production of the proatherogenic mediators MCP-1 and IL-6 in human whole blood, but homocysteine did not. CRP-stimulated production of IL-6, but not MCP-1, was modestly attenuated by short-term treatment with pravastatin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of statin therapy on C-reactive protein levels: the pravastatin inflammation/CRP evaluation (PRINCE): a randomized trial and cohort study.JAMA. 2001 Jul 4;286(1):64-70. doi: 10.1001/jama.286.1.64. JAMA. 2001. PMID: 11434828 Clinical Trial.
-
Changes of plasma inflammatory markers after withdrawal of statin therapy in patients with hyperlipidemia.Clin Chim Acta. 2006 Apr;366(1-2):269-73. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2005.10.021. Epub 2005 Dec 15. Clin Chim Acta. 2006. PMID: 16343471 Clinical Trial.
-
Simvastatin inhibits interleukin-6 release in human monocytes stimulated by C-reactive protein and lipopolysaccharide.Coron Artery Dis. 2003 Jun;14(4):329-34. doi: 10.1097/01.mca.0000078062.22445.60. Coron Artery Dis. 2003. PMID: 12826933
-
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors for lowering elevated levels of C-reactive protein.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2004 Aug 15;61(16):1676-81. doi: 10.1093/ajhp/61.16.1676. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2004. PMID: 15540478 Review.
-
New markers for cardiovascular disease risk in women: impact of endogenous estrogen status and exogenous postmenopausal hormone therapy.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003 Jun;88(6):2470-8. doi: 10.1210/jc.2002-021929. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003. PMID: 12788842 Review.
Cited by
-
ISSLS PRIZE IN CLINICAL SCIENCE 2018: longitudinal analysis of inflammatory, psychological, and sleep-related factors following an acute low back pain episode-the good, the bad, and the ugly.Eur Spine J. 2018 Apr;27(4):763-777. doi: 10.1007/s00586-018-5490-7. Epub 2018 Feb 19. Eur Spine J. 2018. PMID: 29460011
-
An update on the efficacy of anti-inflammatory agents for patients with schizophrenia: a meta-analysis.Psychol Med. 2019 Oct;49(14):2307-2319. doi: 10.1017/S0033291719001995. Epub 2019 Aug 23. Psychol Med. 2019. PMID: 31439071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-inflammatory Strategies for Schizophrenia: A Review of Evidence for Therapeutic Applications and Drug Repurposing.Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2020 Feb 29;18(1):10-24. doi: 10.9758/cpn.2020.18.1.10. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31958901 Free PMC article.
-
Functional roles of polyamines and their metabolite acrolein in eukaryotic cells.Amino Acids. 2021 Oct;53(10):1473-1492. doi: 10.1007/s00726-021-03073-w. Epub 2021 Sep 21. Amino Acids. 2021. PMID: 34546444 Review.
-
A randomized placebo-controlled pilot study of pravastatin as an adjunctive therapy in schizophrenia patients: effect on inflammation, psychopathology, cognition and lipid metabolism.Schizophr Res. 2014 Nov;159(2-3):395-403. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2014.08.021. Epub 2014 Sep 26. Schizophr Res. 2014. PMID: 25261882 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Mayer EL, Jacobsen DW, Robinson K. Homocysteine and coronary atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996;27:517–27. - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM. Role of inflammatory biomarkers in prediction of coronary heart disease. Lancet. 2001;358:946–8. - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM, Cushman M, Stampfer MJ, Tracy RP, Hennekens CH. Inflammation, aspirin, and the risk of cardiovascular disease in apparently healthy men. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:973–9. - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM, Hennekens CH, Buring JE, Rifai N. C-reactive protein and other markers of inflammation in the prediction of cardiovascular disease in women. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:836–43. - PubMed
-
- Stampfer MJ, Malinow MR, Willett WC, Newcomer LM, Upson B, Ullmann D, Tishler PV, Hennekens CH. A prospective study of plasma homocyst(e)ine and risk of myocardial infarction in US physicians. JAMA. 1992;268:877–81. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
