Morphological characteristics of the thalamoperforating arteries
- PMID: 20157376
- PMCID: PMC2817513
- DOI: 10.3340/jkns.2010.47.1.36
Morphological characteristics of the thalamoperforating arteries
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate the morphological characteristics of the thalamoperforating arteries that arise from the P1 segment of the posterior cerebral artery.
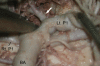
Methods: Thalamoperforating arteries located in the interpeduncular fossa were dissected in 26 formalin-fixed human cadaver brains. We investigated the origin site of thalamoperforating arteries from the P1 segment, number and diameter, and variations in their origin.
Results: Thalamoperforating arteries arose from the superior, posterior or posterosuperior surfaces of the P1 segment at the mean 1.93 mm (range, 0.41-4.71 mm) distance from the basilar apex and entered the brain through the posterior perforated substance. The average number was 3.6 (range 1-8) and mean diameter was 0.70 mm (range 0.24-1.18 mm). Thalamoperforating arteries could be classified into five different types according to their origin at the P1 segment : Type I (bilateral multiple), 38.5%; Type II (unilateral single, unilateral multiple), 26.9%; Type III (bilateral single), 19.2%; Type IV (unilateral single), 11.5%; Type V (unilateral multiple), 3.8%. In 15.4% of all specimens, thalamoperforating arteries arose from the only one side of P1 segment and were not noted in the other side. In such cases, the branches arising from the one side of P1 segment supplied the opposite side.
Conclusion: Variations in the origin of the thalamoperforating arteries should be keep in mind to perform the surgical clipping, endovascular treatment or operation involving the interpeduncular fossa. In particular, unilateral single branch seems to be very risky and significant for surgical technique or endovascular treatment.
Keywords: Cadaver; Morphology; Posterior cerebral artery; Thalamoperforating artery.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Variations in the origin of the thalamoperforating arteries.J Clin Neurosci. 2007 Feb;14(2):134-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2006.01.047. Epub 2006 Nov 17. J Clin Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17113294
-
The artery of Percheron revisited: a cadaveric anatomical study.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2013 Mar;155(3):533-9. doi: 10.1007/s00701-012-1548-1. Epub 2012 Nov 10. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2013. PMID: 23139104
-
Diversity among posterior thalamoperforating branches originated from P1 segment: systematic review.Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2017;76(3):335-339. doi: 10.5603/FM.a2017.0012. Epub 2017 Feb 15. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2017. PMID: 28198523
-
The perforating branches of the P1 segment of the posterior cerebral artery.J Clin Neurosci. 2010 Jan;17(1):80-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2009.03.046. Epub 2009 Dec 16. J Clin Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20006506
-
The Posterior Perforated Substance: A Brain Mystery Wrapped in an Enigma.Curr Top Med Chem. 2019;19(32):2991-2998. doi: 10.2174/1568026619666191127122452. Curr Top Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31775602 Review.
Cited by
-
Thalamo-mesencephalic Branches of the Posterior Cerebral Artery: a 3D Rotational Angiography Study.Clin Neuroradiol. 2024 Sep;34(3):693-701. doi: 10.1007/s00062-024-01418-y. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Clin Neuroradiol. 2024. PMID: 38668868 Free PMC article.
-
Artery of Percheron, an Uncommon Variant of Posterior Cerebral Circulation: A Case Report.Cureus. 2024 Mar 30;16(3):e57266. doi: 10.7759/cureus.57266. eCollection 2024 Mar. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38686254 Free PMC article.
-
A Rare Complication of Pituitary Adenoma Surgery in a Patient with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia 1 Syndrome with Two Novel Genetic Mutations.Asian J Neurosurg. 2020 Dec 21;15(4):1020-1023. doi: 10.4103/ajns.AJNS_100_20. eCollection 2020 Oct-Dec. Asian J Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 33708681 Free PMC article.
-
Uncommon Association of Two Anatomical Variants of Cerebral Circulation: A Fetal-Type Posterior Cerebral Artery and Inferred Artery of Percheron, Complicated with Paramedian Thalamomesencephalic Stroke-Case Presentation and Literature Review.Case Rep Neurol Med. 2018 Sep 24;2018:4567206. doi: 10.1155/2018/4567206. eCollection 2018. Case Rep Neurol Med. 2018. PMID: 30345130 Free PMC article.
-
Ruptured brainstem arteriovenous malformation associated with a thalamoperforating artery aneurysm arising from the P1 segment of the right posterior cerebral artery: illustrative case.J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2023 Oct 9;6(15):CASE23294. doi: 10.3171/CASE23294. Print 2023 Oct 9. J Neurosurg Case Lessons. 2023. PMID: 37910013 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Duret M. Recherches anatomiques sur la circulation de l'encéphale. Arch Phys Norm Path. 1874;1:60–91. (Cited from George AE, Raybaud C, Salamon G, Kricheff II : Anatomy of the thalamoperforating arteries with special emphasis on arteriography of the third ventricles : Part I. Am J Roentgenology 124 : 220-230, 1975)
-
- Duvernoy HM. Human brainstem vessels. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer-Verlag; 1978. pp. 16–23.
-
- George AE, Raybaud C, Salamon G, Kricheff II. Anatomy of the thalamoperforating arteries with special emphasis on arteriography of the third ventricles : Part I. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1975;124:220–230. - PubMed
-
- Grand W, Hopkins LN. The microsurgical anatomy of the basilar artery bifurcation. Neurosurgery. 1977;1:128–131. - PubMed
-
- Hara K, Fujino Y. The thalamoperforate artery. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1966;5:192–200. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

