Roles of dopaminergic d(1) and d(2) receptors in catecholamine release from the rat adrenal medulla
- PMID: 20157389
- PMCID: PMC2817528
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2008.12.1.13
Roles of dopaminergic d(1) and d(2) receptors in catecholamine release from the rat adrenal medulla
Abstract
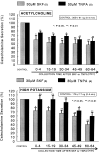
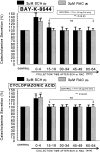
The aim of the present study was designed to establish comparatively the inhibitory effects of D(1)-like and D(2)-like dopaminergic receptor agonists, SKF81297 and R(-)-TNPA on the release of catecholamines (CA) evoked by cholinergic stimulation and membrane depolarization from the isolated perfused model of the rat adrenal medulla. SKF81297 (30microM) and R-(-)-TNPA (30microM) perfused into an adrenal vein for 60 min, produced great inhibition in the CA secretory responses evoked by ACh (5.32x10(- 3) M), DMPP (10(-4) M), McN-A-343 (10(-4) M), high K(+) (5.6x10(-2) M), Bay-K-8644 (10microM), and cyclopiazonic acid (10microM), respectively. For the release of CA evoked by ACh, high K(+), DMPP, McN-A-343, Bay-K-8644 and cyclopiazonic acid, the following rank order of inhibitory potency was obtained: SKF81297>R-(-)-TNPA. However, R(+)-SCH23390, a selectve D(1)-like dopaminergic receptor antagonist, and S(-)-raclopride, a selectve D(2)-like dopaminergic receptor antagonist, enhanced the CA secretory responses evoked by ACh, high K(+), DMPP, McN-A-343, Bay-K-8644 and cyclopiazonic acid only for 0~4 min. The rank order for the enhancement of CA release evoked by high K(+), McN-A-343 and cyclopiazonic acid was R(+)-SCH23390>S(-)-raclopride. Also, the rank order for ACh, DMPP and Bay-K-8644 was S(-)-raclopride > R(+)-SCH23390. Taken together, these results demonstrate that both SKF81297 and R-(-)-TNPA inhibit the CA release evoked by stimulation of cholinergic (both nicotinic and muscarinic) receptors and the membrane depolarization from the isolated perfused rat adrenal gland without affecting the basal release, respectively, but both R(+)-SCH23390 and S(-)-raclopride facilitate the CA release evoked by them. It seems likely that the inhibitory effects of SKF81297 and R-(-)-TNPA are mediated by the activation of D(1)-like and D(2)-like dopaminergic receptors located on the rat adrenomedullary chromaffin cells, respectively, whereas the facilitatory effects of R(+)-SCH23390 and S(-)-raclopride are mediated by the blockade of D(1)-like and D(2)-like dopaminergic receptors, respectively: this action is possibly associated with extra- and intracellular calcium mobilization. Based on these results, it is thought that the presence of dopaminergic D(1) receptors may play an important role in regulation of the rat adrenomedullary CA secretion, in addition to well-known dopaminergic D(2) receptors.
Keywords: Adrenal meduula; Catecholamine secretion; Dopaminergic receptors; R(+)-SCH23390; R-(-)TNPA; S(-)-raclopride; SKF81297.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Inhibitory mechanism of bromocriptine on catecholamine release evoked by cholinergic stimulation and membrane depolarization from the rat adrenal medulla.Arch Pharm Res. 2002 Aug;25(4):511-21. doi: 10.1007/BF02976611. Arch Pharm Res. 2002. PMID: 12214865
-
Influence of lobeline on catecholamine release from the isolated perfused rat adrenal gland.Auton Neurosci. 2004 Jan 30;110(1):27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2003.10.001. Auton Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 14766322
-
Resveratrol inhibits nicotinic stimulation-evoked catecholamine release from the adrenal medulla.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008 Aug;12(4):155-64. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2008.12.4.155. Epub 2008 Aug 31. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 19967050 Free PMC article.
-
Use of isolated chromaffin cells to study basic release mechanisms.J Auton Nerv Syst. 1983 Jan;7(1):59-86. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(83)90069-3. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1983. PMID: 6188774 Review.
-
GABAA receptor: a unique modulator of excitability, Ca2+ signaling, and catecholamine release of rat chromaffin cells.Pflugers Arch. 2018 Jan;470(1):67-77. doi: 10.1007/s00424-017-2080-1. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Pflugers Arch. 2018. PMID: 29101464 Review.
References
-
- Akaike A, Mine Y, Sasa M, Takaori S. Voltage and current clamp studies of muscarinic and nicotinic excitation of the rat adrenal chromaffin cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990;255:333–339. - PubMed
-
- Albillos A, Abad F, Garcia AG. Cross-talk between M2 muscarinic and D1 dopamine receptors in the cat adrenal medulla. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992;183:1019–1024. - PubMed
-
- Andersen PH, Jansen JA. Dopamine receptor agonists: selectivity and D1 receptor efficacy. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990;188:335–347. - PubMed
-
- Anton AH, Sayre DF. A study of the factors affecting the aluminum oxidetrihydroxy indole procedure for the analysis of catecholamines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1962;138:360–375. - PubMed
-
- Artalejo CR, Ariano MA, Perlman RL, Fox AP. Activation of facilitation calcium channels in chromaffin cells by D1 dopamine receptors through a AMP/protein Kinase A-dependent mechanism. Nature. 1990;348:239–242. - PubMed

