White Matter Damage and Hippocampal Neurodegeneration Induced by Permanent Bilateral Occlusion of Common Carotid Artery in the Rat: Comparison between Wistar and Sprague-Dawley Strain
- PMID: 20157400
- PMCID: PMC2817551
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2008.12.3.89
White Matter Damage and Hippocampal Neurodegeneration Induced by Permanent Bilateral Occlusion of Common Carotid Artery in the Rat: Comparison between Wistar and Sprague-Dawley Strain
Abstract
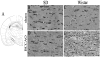
In order to reproduce chronic cerebral hypoperfusion as it occurs in human aging and Alzheimer's disease, we introduced permanent, bilateral occlusion of the common carotid arteries (BCCAO) in rats (Farkas et al, 2007). Here, we induced BCCAO in two different rat strains in order to determine whether there was a strain difference in the pathogenic response to BCCAO. Male Wistar and Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats (250-270 g) were subjected to BCCAO for three weeks. Klüver-Barrera and cresyl violet staining were used to evaluate white matter and gray matter damage, respectively. Wistar rats had a considerably higher mortality rate (four of 14 rats) as compared to SD rats (one of 15 rats) following BCCAO. Complete loss of pupillary light reflex occurred in all Wistar rats that survived, but loss of pupillary light reflex did not occur at all in SD rats. Moreover, BCCAO induced marked vacuolation in the optic tract of Wistar rats as compared to SD rats. In contrast, SD rats showed fewer CA1 hippocampal neurons than Wistar rats following BCCAO. These results suggest that the neuropathological process induced by BCCAO takes place in a region-specific pattern that varies according to the strain of rat involved.
Keywords: Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion; Hippocampal neurodegeneration; Rat; Sprague-Dawley strain; White matter damage; Wistar strain.
Figures


References
-
- Butte DM, Fortin T, Pappas BA. Pinealectomy: behavioral and neuropathological consequences in a chronic cerebral hypoperfusion model. Neurobiol Aging. 2002;23:309–317. - PubMed
-
- Bennett SA, Tenniswood M, Chen JH, Davidson CM, Keyes MT, Fortin T, Pappas A. Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion elicits neuronal apoptosis and behavioral impairment. Neuroreport. 1998;9:164–166. - PubMed
-
- Cho KO, La HO, Cho YJ, Sung KW, Kim SY. Minocycline attenuates white matter damage in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. J Neurosci Res. 2006;83:285–291. - PubMed
-
- Davidson CM, Pappas BA, Stevens WD, Fortin T, Bennett SAL. Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion: loss of pupillary reflex, visual impairment and retinal neurodegeneration. Brain Res. 2000;859:96–103. - PubMed
-
- Farkas E, Institoris A, Domoki F, Mihaly A, Bari F. The effect of pre- and post-treatment with diazoxide on the early phase of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in the rat. Brain Res. 2006;1087:168–174. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

