Influence of ketamine on catecholamine secretion in the perfused rat adrenal medulla
- PMID: 20157402
- PMCID: PMC2817547
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2008.12.3.101
Influence of ketamine on catecholamine secretion in the perfused rat adrenal medulla
Abstract
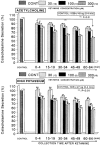
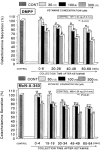
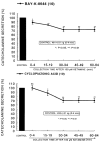
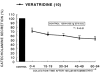
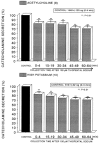
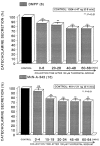
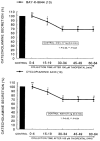
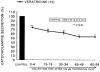
The aim of the present study was to examine the effects of ketamine, a dissociative anesthetics, on secretion of catecholamines (CA) secretion evoked by cholinergic stimulation from the perfused model of the isolated rat adrenal gland, and to establish its mechanism of action, and to compare ketamine effect with that of thiopental sodium, which is one of intravenous barbiturate anesthetics. Ketamine (30~300microM), perfused into an adrenal vein for 60 min, dose- and time-dependently inhibited the CA secretory responses evoked by ACh (5.32 mM), high K(+) (a direct membrane-depolarizer, 56 mM), DMPP (a selective neuronal nicotinic NN receptor agonist, 100microM) and McN-A-343 (a selective muscarinic M1 receptor agonist, 100microM). Also, in the presence of ketamine (100microM), the CA secretory responses evoked by veratridine (a voltage-dependent Na(+) channel activator, 100microM), Bay-K-8644 (an L-type dihydropyridine Ca(2+) channel activator, 10microM), and cyclopiazonic acid (a cytoplasmic Ca(2+)-ATPase inhibitor, 10microM) were significantly reduced, respectively. Interestingly, thiopental sodium (100microM) also caused the inhibitory effects on the CA secretory responses evoked by ACh, high K(+) , DMPP, McN-A-343, veratridine, Bay-K-8644, and cyclopiazonic acid. Collectively, these experimental results demonstrate that ketamine inhibits the CA secretion evoked by stimulation of cholinergic (both nicotinic and muscarinic) receptors and the membrane depolarization from the isolated perfused rat adrenal gland. It seems likely that the inhibitory effect of ketamine is mediated by blocking the influx of both Ca(2+) and Na(+) through voltage-dependent Ca(2+) and Na(+) channels into the rat adrenal medullary chromaffin cells as well as by inhibiting Ca(2+) release from the cytoplasmic calcium store, which are relevant to the blockade of cholinergic receptors. It is also thought that, on the basis of concentrations, ketamine causes similar inhibitory effect with thiopental in the CA secretion from the perfused rat adrenal medulla.
Keywords: Adrenal medulla; Catecholamine secretion; Cholinergic receptors; Ketamine; thiopental.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Resveratrol inhibits nicotinic stimulation-evoked catecholamine release from the adrenal medulla.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008 Aug;12(4):155-64. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2008.12.4.155. Epub 2008 Aug 31. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 19967050 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory Effects of Total Ginseng Saponin on Catecholamine Secretion from the Perfused Adrenal Medulla of SHRs.J Ginseng Res. 2011 Jun;35(2):176-90. doi: 10.5142/jgr.2011.35.2.176. J Ginseng Res. 2011. PMID: 23717060 Free PMC article.
-
Provinol inhibits catecholamine secretion from the rat adrenal medulla.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009 Jun;13(3):229-39. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2009.13.3.229. Epub 2009 Jun 30. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19885042 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effects of olmesartan on catecholamine secretion from the perfused rat adrenal medulla.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010 Aug;14(4):241-8. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.4.241. Epub 2010 Aug 31. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20827339 Free PMC article.
-
Use of isolated chromaffin cells to study basic release mechanisms.J Auton Nerv Syst. 1983 Jan;7(1):59-86. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(83)90069-3. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1983. PMID: 6188774 Review.
Cited by
-
The relation between the effect of a subhypnotic dose of thiopental on claw pain threshold in rats and adrenalin, noradrenalin and dopamine levels.Exp Anim. 2015;64(4):391-6. doi: 10.1538/expanim.15-0028. Epub 2015 Jul 22. Exp Anim. 2015. PMID: 26211784 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of ketamine and thiopental used alone or in combination on the brain, heart, and bronchial tissues of rats.Arch Med Sci. 2018 Apr;14(3):645-654. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2016.59508. Epub 2016 Jun 6. Arch Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 29765454 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akaike A, Mine Y, Sasa M, Takaori S. Voltage and current clamp studies of muscarinic and nicotinic excitation of the rat adrenal chromaffin cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990;255:333–339. - PubMed
-
- Anton AH, Sayre DF. A study of the factors affecting the aluminum oxidetrihydroxy indole procedure for the analysis of catecholamines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1962;138:360–375. - PubMed
-
- Azzaro AJ, Smith DJ. The inhibitory action of ketamine HCl on [3H]5-hydroxytryptamine accumulation by rat brain synaptosomal-rich fractions: comparison with [3H]catecholamine and [3H]γ-aminobutyric acid uptake. Neuropharmacology. 1977;16:349–356. - PubMed
-
- Burgoyne RD. Mechanisms of secretion from adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984;779:201–216. - PubMed
-
- Cena V, Nicolas GP, Sanchez-Garcia P, Kirpekar SM, Garcia AG. Pharmacological dissection of receptor-associated and voltage-sensitive ionic channels involved in catecholamine release. Neuroscience. 1983;10:1455–1462. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

