(-)-epigallocatechin gallate inhibits the pacemaker activity of interstitial cells of cajal of mouse small intestine
- PMID: 20157403
- PMCID: PMC2817548
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2008.12.3.111
(-)-epigallocatechin gallate inhibits the pacemaker activity of interstitial cells of cajal of mouse small intestine
Abstract
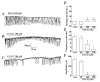
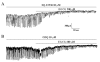
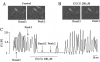
The effects of (-)-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) on pacemaker activities of cultured interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) from murine small intestine were investigated using whole-cell patch-clamp technique at 30 and Ca(2+) image analysis. ICC generated spontaneous pacemaker currents at a holding potential of -70 mV. The treatment of ICC with EGCG resulted in a dose-dependent decrease in the frequency and amplitude of pacemaker currents. SQ-22536, an adenylate cyclase inhibitor, and ODQ, a guanylate cyclase inhibitor, did not inhibit the effects of EGCG. EGCG-induced effects on pacemaker currents were not inhibited by glibenclamide, an ATP-sensitive K(+) channel blocker and TEA, a Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channel blocker. Also, we found that EGCG inhibited the spontaneous [Ca(2+)](i) oscillations in cultured ICC. In conclusion, EGCG inhibited the pacemaker activity of ICC and reduced [Ca(2+)](i) oscillations by cAMP-, cGMP-, ATP-sensitive K+ channel-independent manner.
Keywords: (-)-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG); Interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC); Intestinal motility; Pacemaker currents.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Phentolamine inhibits the pacemaker activity of mouse interstitial cells of Cajal by activating ATP-sensitive K+ channels.Arch Pharm Res. 2010 Mar;33(3):479-89. doi: 10.1007/s12272-010-0319-x. Epub 2010 Mar 30. Arch Pharm Res. 2010. PMID: 20361315
-
Noradrenaline inhibits pacemaker currents through stimulation of beta 1-adrenoceptors in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal from murine small intestine.Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Feb;141(4):670-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705665. Epub 2004 Jan 26. Br J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 14744802 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay of hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide on the pacemaker activity of interstitial cells of cajal from mouse small intestine.Chonnam Med J. 2011 Aug;47(2):72-9. doi: 10.4068/cmj.2011.47.2.72. Epub 2011 Aug 31. Chonnam Med J. 2011. PMID: 22111064 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of pacemaker currents by nitric oxide via activation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal from the mouse small intestine.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2007 Nov;376(3):175-84. doi: 10.1007/s00210-007-0187-1. Epub 2007 Oct 12. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17932655
-
Regulation of pacemaker currents in interstitial cells of Cajal from murine small intestine by cyclic nucleotides.J Physiol. 2000 Aug 15;527 Pt 1(Pt 1):149-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.00149.x. J Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10944178 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alvarez-Castro E, Campos-Toimil M, Orallo F. (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces contraction of the rat aorta by a calcium influx-dependent mechanism. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2004;369:496–506. - PubMed
-
- Aoyama M, Yamada A, Wang J, Ohya S, Furuzono S, Goto T, Hotta S, Ito Y, Matsubara T, Shimokata K, Chen SR, Imaizumi Y, Nakayama S. Requirement of ryanodine receptors for pacemaker Ca2+ activity in ICC in HEK293 cells. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:2813–2825. - PubMed
-
- Baek WK, Jang BC, Lim JH, Kwon TK, Lee HY, Cho CH, Kim DK, Shin DH, Park JG, Lim JG, Bae JH, Bae JH, Yoo SK, Park WK, Song DK. Inhibitory modulation of ATP-sensitive potassium channels by gallate-ester moiety of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Biochem Pharm. 2005;70:1560–1567. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

