Unicystic ameloblastoma of the mandible--an unusual case report and review of literature
- PMID: 20157425
- PMCID: PMC2821325
- DOI: 10.1186/1758-3284-2-1
Unicystic ameloblastoma of the mandible--an unusual case report and review of literature
Abstract
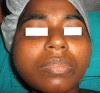
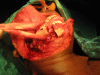
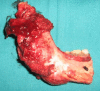
Ameloblastoma is a true neoplasm of odontogenic epithelial origin. It is the second most common odontogenic neoplasm, and only odontoma outnumbers it in reported frequency of occurrence. Its incidence, combined with its clinical behavior, makes ameloblastoma the most significant odontogenic neoplasm. Unicystic ameloblastoma (UA) refers to those cystic lesions that show clinical, radiographic, or gross features of a mandibular cyst, but on histologic examination show a typical ameloblastomatous epithelium lining part of the cyst cavity, with or without luminal and/or mural tumor growth. It accounts for 5-15% of all intraosseous ameloblastomas. We report a case of unicystic ameloblastoma in a 30-year-old female, and review the literature.
Figures
References
-
- Kahairi A, Ahmad RL, Wan Islah L, Norra H. Management of large mandibular ameloblastoma - a case report and literature reviews. Archives of Orofacial Sciences. 2008;3(2):52–55.
-
- Philipsen HP, Reichart PA. Odontogenic tumors and allied lesions. Quintessence Pub. Co. Ltd; 2004. Classification of odontogenic tumors and allied lesions; pp. 21–3.
-
- Chana, Jagdeep S, Yang-Ming Chang, Wei, Fu-Chan, Shen, Yu-Fen, Chan Chiu-Po, Lin Hsiu-Na, Tsai Chi-Ying, Jeng Seng-Feng. Segmental mandibulectomy and immediate free fibula osteoseptocutaneous flap reconstruction with endosteal implants: An ideal treatment method for mandibular ameloblastoma. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004;113(1):80–87. doi: 10.1097/01.PRS.0000097719.69616.29. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Philipsen HP, Reichart PA. Odontogenic tumors and allied lesions. London: Quintessence Pub. Co. Ltd; 2004. Unicystic ameloblastoma; pp. 77–86.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources