Anti-inflammatory effects of antidepressant and atypical antipsychotic medication for the treatment of major depression and comorbid arthritis: a case report
- PMID: 20157432
- PMCID: PMC2821395
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-1947-4-6
Anti-inflammatory effects of antidepressant and atypical antipsychotic medication for the treatment of major depression and comorbid arthritis: a case report
Abstract
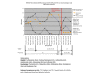
Introduction: This case report describes the effects of psychotropic treatment, quetiapine in particular, on systemic inflammation, pain, general functioning and major depression in the treatment of a woman with arthritis.
Case presentation: A 49-year-old Caucasian Australian woman with arthritis, pain and depression was treated with a course of escitalopram, mirtazapine and quetiapine. Pain levels, general functioning and degree of depressive symptoms were evaluated with a visual analogue scale. Systemic inflammation had been assessed by C-reactive protein serum levels since 2003. C-reactive protein levels, physical pain, symptoms of arthritis and depression decreased significantly during the past 12 months of treatment with quetiapine, while treatment with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and mirtazapine remained the same.
Conclusions: We suggest that the treatment particularly with quetiapine may have anti-inflammatory effects in arthritis and comorbid major depression, which eventually led to a remission of pain and depression and to normal general function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Using antipsychotic agents in older patients.J Clin Psychiatry. 2004;65 Suppl 2:5-99; discussion 100-102; quiz 103-4. J Clin Psychiatry. 2004. PMID: 14994733 Review.
-
Rhabdomyolysis Associated With Mirtazapine and Quetiapine Therapy: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Cureus. 2024 Feb 1;16(2):e53428. doi: 10.7759/cureus.53428. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38435137 Free PMC article.
-
Quetiapine for insomnia associated with refractory depression exacerbated by phenelzine.Ann Pharmacother. 2006 Mar;40(3):567-70. doi: 10.1345/aph.1G416. Epub 2006 Feb 14. Ann Pharmacother. 2006. PMID: 16478812
-
The antidepressant- and anxiolytic-like effects following co-treatment with escitalopram and risperidone in rats.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016 Jun;67(3):471-80. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27512008
-
Treating comorbid anxiety and depression: Psychosocial and pharmacological approaches.World J Psychiatry. 2015 Dec 22;5(4):366-78. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v5.i4.366. eCollection 2015 Dec 22. World J Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26740928 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrating neuroimmune systems in the neurobiology of depression.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016 Aug;17(8):497-511. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2016.69. Epub 2016 Jun 9. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27277867 Review.
-
Evaluation of Arterial Stiffness in Depression Patients.Alpha Psychiatry. 2023 Sep 1;24(5):193-199. doi: 10.5152/alphapsychiatry.2023.221099. eCollection 2023 Sep. Alpha Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 38105785 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell immune profiling reveals broad anti-inflammation response in bipolar disorder patients with quetiapine and valproate treatment.iScience. 2023 Jun 7;26(7):107057. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107057. eCollection 2023 Jul 21. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37534158 Free PMC article.
-
Acacia saligna extract alleviates quetiapine-induced sexual toxicity in male albino rats: Insights from UPLC-MS/MS metabolite profiling, structural and PI3K/NF-κB pathway assessments.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 3;10(13):e33993. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33993. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39071580 Free PMC article.
-
Quetiapine ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis in mice via the suppression of the AKT and ERK signaling pathways.Inflamm Res. 2018 Oct;67(10):847-861. doi: 10.1007/s00011-018-1176-1. Epub 2018 Aug 14. Inflamm Res. 2018. PMID: 30109356
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

