The regulation of brain states by neuroactive substances distributed via the cerebrospinal fluid; a review
- PMID: 20157443
- PMCID: PMC2821375
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-8454-7-1
The regulation of brain states by neuroactive substances distributed via the cerebrospinal fluid; a review
Abstract
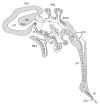
The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) system provides nutrients to and removes waste products from the brain. Recent findings suggest, however, that in addition, the CSF contains message molecules in the form of actively released neuroactive substances. The concentrations of these vary between locations, suggesting they are important for the changes in brain activity that underlie different brain states, and induce different sensory input and behavioral output relationships.The cranial CSF displays a rapid caudally-directed ventricular flow followed by a slower rostrally-directed subarachnoid flow (mainly towards the cribriform plate and from there into the nasal lymphatics). Thus, many brain areas are exposed to and can be influenced by substances contained in the CSF. In this review we discuss the production and flow of the CSF, including the mechanisms involved in the regulation of its composition. In addition, the available evidence for the release of neuropeptides and other neuroactive substances into the CSF is reviewed, with particular attention to the selective effects of these on distant downstream receptive brain areas. As a conclusion we suggest that (1) the flowing CSF is involved in more than just nutrient and waste control, but is also used as a broadcasting system consisting of coordinated messages to a variety of nearby and distant brain areas; (2) this special form of volume transmission underlies changes in behavioral states.
Figures

References
-
- Frijda N. The laws of emotions. London: Psychology Press; 2007.
-
- Hinde RA. Animal Behaviour; A Synthesis of Ethology and Comparative Psychology. second. New York: McGRAW-Hill Book Cy; 1970.
-
- Mogenson GJ. The neurobiology of Behavior: an introduction. Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 1977.
-
- Panksepp J. Affective Neuroscience, The foundations of human and animal emotions. New York: Oxford University Press; 1998.
-
- Swanson LW. Brain Architecture, understanding the basic plan. New York: Oxford University Press; 2003.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

