The Prion Disease Database: a comprehensive transcriptome resource for systems biology research in prion diseases
- PMID: 20157484
- PMCID: PMC2790306
- DOI: 10.1093/database/bap011
The Prion Disease Database: a comprehensive transcriptome resource for systems biology research in prion diseases
Abstract
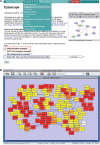
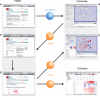
Prion diseases reflect conformational conversion of benign isoforms of prion protein (PrP(C)) to malignant PrP(Sc) isoforms. Networks perturbed by PrP(Sc) accumulation and their ties to pathological events are poorly understood. Time-course transcriptomic and phenotypic data in animal models are critical for understanding prion-perturbed networks in systems biology studies. Here, we present the Prion Disease Database (PDDB), the most comprehensive data resource on mouse prion diseases to date. The PDDB contains: (i) time-course mRNA measurements spanning the interval from prion inoculation through appearance of clinical signs in eight mouse strain-prion strain combinations and (ii) histoblots showing temporal PrP(Sc) accumulation patterns in brains from each mouse-prion combination. To facilitate prion research, the PDDB also provides a suite of analytical tools for reconstructing dynamic networks via integration of temporal mRNA and interaction data and for analyzing these networks to generate hypotheses.Database URL:http://prion.systemsbiology.net.
Figures

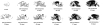
References
-
- Hood L, Heath JR, Phelps ME, et al. Systems biology and new technologies enable predictive and preventative medicine. Science. 2004;306:640–643. - PubMed
-
- Lin B, White JT, Lu W, et al. Evidence for the presence of disease-perturbed networks in prostate cancer cells by genomic and proteomic analyses: a systems approach to disease. Cancer Res. 2005;65:3081–3091. - PubMed
-
- Price ND, Edelman L, Lee I, et al. Systems biology and the emergence of systems medicine. In: Willard HF, Ginsburg GS, editors. Genomic and Personalized Medicine: From Principles to Practice. I. New York: Academic Press; 2009. pp. 74–85.
-
- Prusiner SB. Prion Biology and Diseases. 2nd. 2003. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, pp. 1–88. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

