Meiotic Recombination in Schizosaccharomyces pombe: A Paradigm for Genetic and Molecular Analysis
- PMID: 20157622
- PMCID: PMC2820269
- DOI: 10.1007/7050_2007_025
Meiotic Recombination in Schizosaccharomyces pombe: A Paradigm for Genetic and Molecular Analysis
Abstract
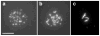
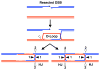
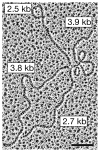
The fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe is especially well-suited for both genetic and biochemical analysis of meiotic recombination. Recent studies have revealed ~50 gene products and two DNA intermediates central to recombination, which we place into a pathway from parental to recombinant DNA. We divide recombination into three stages - chromosome alignment accompanying nuclear "horsetail" movement, formation of DNA breaks, and repair of those breaks - and we discuss the roles of the identified gene products and DNA intermediates in these stages. Although some aspects of recombination are similar to those in the distantly related budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, other aspects are distinctly different. In particular, many proteins required for recombination in one species have no clear ortholog in the other, and the roles of identified orthologs in regulating recombination often differ. Furthermore, in S. pombe the dominant joint DNA molecule intermediates contain single Holliday junctions, and intersister joint molecules are more frequent than interhomolog types, whereas in S. cerevisiae interhomolog double Holliday junctions predominate. We speculate that meiotic recombination in other organisms shares features of each of these yeasts.
Figures

References
-
- Allers T, Lichten M. Differential timing and control of noncrossover and crossover recombination during meiosis. Cell. 2001;106:47–57. - PubMed
-
- Bishop DK, Park D, Xu L, Kleckner N. DMC1: A meiosis-specific homolog of E. coli recA required for recombination, synaptonemal complex formation, and cell cycle progression. Cell. 1992;69:439–456. - PubMed
-
- Boddy MN, Gaillard P-HL, McDonald WH, Shanahan P, Yates JR, Russell P. Mus81-Eme1 are essential components of a Holliday junction resolvase. Cell. 2001;107:537–548. - PubMed
-
- Borde V, Goldman ASH, Lichten M. Direct coupling between meiotic DNA replication and recombination initiation. Science. 2000;290:806–809. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
