Investigation of Mediational Processes Using Parallel Process Latent Growth Curve Modeling
- PMID: 20157639
- PMCID: PMC2821108
- DOI: 10.1207/S15328007SEM1002_5
Investigation of Mediational Processes Using Parallel Process Latent Growth Curve Modeling
Abstract
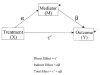
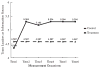
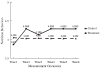
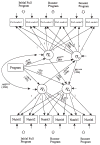
This study investigated a method to evaluate mediational processes using latent growth curve modeling. The mediator and the outcome measured across multiple time points were viewed as 2 separate parallel processes. The mediational process was defined as the independent variable influencing the growth of the mediator, which, in turn, affected the growth of the outcome. To illustrate modeling procedures, empirical data from a longitudinal drug prevention program, Adolescents Training and Learning to Avoid Steroids, were used. The program effects on the growth of the mediator and the growth of the outcome were examined first in a 2-group structural equation model. The mediational process was then modeled and tested in a parallel process latent growth curve model by relating the prevention program condition, the growth rate factor of the mediator, and the growth rate factor of the outcome.
Figures

References
-
- Ajzen I, Madden TJ. Prediction of goal-directed behavior: Attitudes, intentions, and perceived behavioral control. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology. 1986;22:453–474.
-
- Arbuckle JL. Full information estimation in the presence of incomplete data. In: Marcoulides GA, Schumacker RE, editors. Advanced structural equation modeling: Issues and techniques. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc; 1996. pp. 243–277.
-
- Aroian LA. The probability function of the product of two normally distributed variables. Annals of Mathematical Statistics. 1947;18:265–271.
-
- Bandura A. Social learning theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall; 1977.
-
- Baron RM, Kenny DA. The moderator–mediator distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1986;51:1173–1182. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
