EPR and ENDOR Investigation of Rhodosemiquinone in Bacterial Reaction Centers Formed by B-Branch Electron Transfer
- PMID: 20157643
- PMCID: PMC2821119
- DOI: 10.1007/s00723-009-0042-2
EPR and ENDOR Investigation of Rhodosemiquinone in Bacterial Reaction Centers Formed by B-Branch Electron Transfer
Abstract
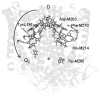
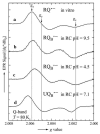
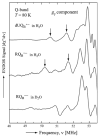
In photosynthetic bacteria, light-induced electron transfer takes place in a protein called the reaction center (RC) leading to the reduction of a bound ubiquinone molecule, Q(B), coupled with proton binding from solution. We used electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) and electron-nuclear double resonance (ENDOR) to study the magnetic properties of the protonated semiquinone, an intermediate proposed to play a role in proton coupled electron transfer to Q(B). To stabilize the protonated semiquinone state, we used a ubiquinone derivative, rhodoquinone, which as a semiquinone is more easily protonated than ubisemiquinone. To reduce this low-potential quinone we used mutant RCs modified to directly reduce the quinone in the Q(B) site via B-branch electron transfer (Paddock et al. in Biochemistry 44:6920-6928, 2005). EPR and ENDOR signals were observed upon illumination of mutant RCs in the presence of rhodoquinone. The EPR signals had g values characteristic of rhodosemiquinone (g(x) = 2.0057, g(y) = 2.0048, g(z) ∼ 2.0018) at pH 9.5 and were changed at pH 4.5. The ENDOR spectrum showed couplings due to solvent exchangeable protons typical of hydrogen bonds similar to, but different from, those found for ubisemiquinone. This approach should be useful in future magnetic resonance studies of the protonated semiquinone.
Figures
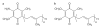
References
-
- Blankenship RE. Molecular Mechanisms of Photosynthesis. Blackwell; London: 2002.
-
- Feher G, Allen JP, Okamura MY, Rees DC. Nature (London) 1989;339:111–116.
-
- Gunner M. Curr Top Bioenerg. 1991;16:319–367.
-
- Okamura MY, Feher G. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:861–896. - PubMed
-
- Wraight C, Gunner M. In: Advances in Photosynthesis and Photorespiration. Hunter CN, Daldal F, Thurnauer MC, Beatty JT, editors. Vol. 28. Springer; Dordrecht: 2009. pp. 379–405.
