Crossing paths: interactions between the cell death machinery and growth factor survival signals
- PMID: 20157838
- PMCID: PMC11115775
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-010-0288-8
Crossing paths: interactions between the cell death machinery and growth factor survival signals
Abstract
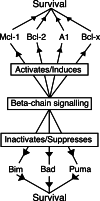
Cytokines and growth factors play a crucial role in the maintenance of haematopoietic homeostasis. They transduce signals that regulate the competing commitments of haematopoietic stem cells, quiescence or proliferation, retention of stem cell pluripotency or differentiation, and survival or demise. When the balance between these commitments and the requirements of the organisms is disturbed, particularly when it favours survival and proliferation, cancer may result. Cell death provoked by loss of growth factor signalling is regulated by the Bcl-2 family of apoptosis regulators, and thus survival messages transduced by growth factors must regulate the activity of these proteins. Many aspects of direct interactions between cytokine signalling and regulation of apoptosis remain elusive. In this review, we explore the mechanisms by which cytokines, in particular Interleukin-3 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, promote cell survival and suppress apoptosis as models of how cytokine signalling and apoptotic pathways intersect.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Two distinct interleukin-3-mediated signal pathways, Ras-NFIL3 (E4BP4) and Bcl-xL, regulate the survival of murine pro-B lymphocytes.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Apr;19(4):2754-62. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.4.2754. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10082541 Free PMC article.
-
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) induces antiapoptotic and proapoptotic signals in acute myeloid leukemia.Blood. 2003 Jul 15;102(2):630-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-06-1890. Epub 2003 Mar 27. Blood. 2003. PMID: 12663443
-
Downregulation of Bim, a proapoptotic relative of Bcl-2, is a pivotal step in cytokine-initiated survival signaling in murine hematopoietic progenitors.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Feb;21(3):854-64. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.3.854-864.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11154272 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt signalling in stem cells and cancer.Nature. 2005 Apr 14;434(7035):843-50. doi: 10.1038/nature03319. Nature. 2005. PMID: 15829953 Review.
-
The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival.Science. 1998 Aug 28;281(5381):1322-6. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5381.1322. Science. 1998. PMID: 9735050 Review.
Cited by
-
Over Fifty Years of Life, Death, and Cannibalism: A Historical Recollection of Apoptosis and Autophagy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 18;22(22):12466. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212466. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between the rs1800795G>C polymorphism in the promoter of interleukin-6 gene and bladder cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018 Jul 1;11(7):3598-3604. eCollection 2018. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018. PMID: 31949739 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of IKK2 in haematopoietic cells of adult mice leads to elevated interleukin-6, neutrophilia and fatal gastrointestinal inflammation.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Jan 4;12(1):28. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03298-9. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33414459 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms and cross-talk of regulated cell death and their epigenetic modifications in tumor progression.Mol Cancer. 2024 Nov 29;23(1):267. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02172-y. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39614268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Different types of cell death and their shift in shaping disease.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Aug 4;9(1):284. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01581-0. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 37542066 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stanley E, Lieschke GJ, Grail D, Metcalf D, Hodgson G, Gall JA, Maher DW, Cebon J, Sinickas V, Dunn AR. Granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor-deficient mice show no major perturbation of hematopoiesis but develop a characteristic pulmonary pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:5592–5596. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5592. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dranoff G, Mulligan RC. Activities of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor revealed by gene transfer and gene knockout studies. Stem Cells. 1994;12:173–182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

