Dose effects of triazolam and alcohol on cognitive performance in healthy volunteers
- PMID: 20158290
- PMCID: PMC2847582
- DOI: 10.1037/a0018407
Dose effects of triazolam and alcohol on cognitive performance in healthy volunteers
Abstract
Benzodiazepines and alcohol are widely used psychoactive substances that have performance-impairing effects. Research suggests that the impairment profiles for benzodiazepines and alcohol differ, although few cognitive psychopharmacological studies have directly compared these drugs. This double-blind, double-dummy, placebo-controlled, repeated measures study directly compared the acute dose effects of triazolam (0.125, 0.25 mg/70 kg) and alcohol (0.40, 0.80 g/kg) in 20 social drinkers. At doses that produced comparable psychomotor impairment, triazolam was more likely to impair several objective measures of cognitive performance (e.g., episodic memory, divided attention) and to slow performance across several measures. However, only alcohol impaired accuracy on the digit symbol substitution and semantic memory tasks. In addition to objective measures, both drugs impaired awareness of performance impairments (i.e., metacognition) such that participants overestimated impairment, and the magnitude of this effect was generally larger for alcohol. Only triazolam impaired other measures of metacognition (e.g., error detection on a choice reaction time task). Future research might examine the clinical implications of the performance impairments reported here given the widespread use of benzodiazepines and alcohol.
(PsycINFO Database Record (c) 2010 APA, all rights reserved).
Figures


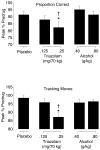
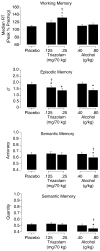
References
-
- Acons K, Chan L, Drummond G, Tiplady B. Effects of ethanol and promethazine on awareness of errors and judgements of performance. Journal of Psychopharmacology. 2006;20(5):661–669. - PubMed
-
- Bacon E, Danion JM, Kauffmann-Muller F, Schelstraete MA, Bruant A, Sellal F, Grange D. Confidence level and feeling of knowing for episodic and semantic memory: an investigation of lorazepam effects on metamemory. Psychopharmacology. 1998;138:318–25. - PubMed
-
- Bacon E, Schwartz BL, Paire-Ficout L, Izaute M. Dissociation between the cognitive process and the phenomenological experience of TOT: Effect of the anxiolytic drug lorazepam on TOT states. Consciousness and Cognition. 2007;16:360–373. - PubMed
-
- Baddeley AD. Essentials of human memory. UK: Psychology Press, Ltd; 1999.

