Efficacy and safety of 1-month postpartum zidovudine-didanosine to prevent HIV-resistance mutations after intrapartum single-dose nevirapine
- PMID: 20158398
- PMCID: PMC2922986
- DOI: 10.1086/650745
Efficacy and safety of 1-month postpartum zidovudine-didanosine to prevent HIV-resistance mutations after intrapartum single-dose nevirapine
Abstract
Background: Intrapartum single-dose nevirapine plus third trimester maternal and infant zidovudine are essential components of programs to prevent mother-to-child transmission of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in resource-limited settings. The persistence of nevirapine in the plasma for 3 weeks postpartum risks selection of resistance mutations to nonnucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs). We hypothesized that a 1-month zidovudine-didanosine course initiated at the same time as single-dose nevirapine (sdNVP) would prevent the selection of nevirapine-resistance mutations.
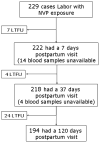
Methods: HIV-infected pregnant women in the PHPT-4 cohort with CD4 cell counts >250 cells/mm3 received antepartum zidovudine from the third trimester until delivery, sdNVP during labor, and a 1-month zidovudine-didanosine course after delivery. These women were matched on the basis of baseline HIV load, CD4 cell count, and duration of antepartum zidovudine to women who received sdNVP in the PHPT-2 trial (control subjects). Consensus sequencing and the more sensitive oligonucleotide ligation assay were performed on samples obtained on postpartum days 7-10, 37-45, and 120 (if the HIV load was >500 copies/mL) to detect K103N/Y181C/G190A mutations.
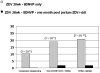
Results: The 222 PHPT-4 subjects did not differ from matched control subjects in baseline characteristics except for age. The combined group median CD4 cell count was 421 cells/mm3 (interquartile range [IQR], 322-549 cells/mm3), the median HIV load was 3.45 log10 copies/mL (IQR, 2.79-4.00 log10 copies/mL), and the median duration of zidovudine prophylaxis was 10.4 weeks (IQR, 9.1-11.4 weeks). Using consensus sequencing, major NNRTI resistance mutations were detected after delivery in 0% of PHPT-4 subjects and 10.4% of PHPT-2 controls. The oligonucleotide ligation assay detected resistance in 1.8% of PHPT-4 subjects and 18.9% of controls. Major NNRTI resistance mutations were detected by either method in 1.8% of PHPT-4 subjects and 20.7% of controls (P < .001).
Conclusions: A 1-month postpartum course of zidovudine plus didanosine prevented the selection of the vast majority of NNRTI resistance mutations.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflict of interest: All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Another milestone in minimizing risks to mothers exposed to single-dose nevirapine for prevention of vertical transmission of HIV-1 to infants: what next?Clin Infect Dis. 2010 Mar 15;50(6):909-11. doi: 10.1086/650746. Clin Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20158399 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lallemant M, Jourdain G, Le Coeur S, et al. Single-dose perinatal nevirapine plus standard zidovudine to prevent mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1 in Thailand. N Engl J Med. 2004 Jul 15;351(3):217–28. - PubMed
-
- Mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 2005 Feb 1;40(3):458–65. - PubMed
-
- Dorenbaum A, Cunningham CK, Gelber RD, et al. Two-dose intrapartum/newborn nevirapine and standard antiretroviral therapy to reduce perinatal HIV transmission: a randomized trial. Jama. 2002 Jul 10;288(2):189–98. - PubMed
-
- Warszawski J, Tubiana R, Le Chenadec J, et al. Mother-to-child HIV transmission despite antiretroviral therapy in the ANRS French Perinatal Cohort. AIDS. 2008 Jan 11;22(2):289–99. - PubMed
-
- Recommendations for a public health approach. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2006. Aug 7, Antiretroviral drugs for treating pregnant women and preventing HIV infection in infants: towards universal access. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials