Temperament and the environment in the etiology of childhood anxiety
- PMID: 20158575
- PMCID: PMC2884043
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.2010.02228.x
Temperament and the environment in the etiology of childhood anxiety
Abstract
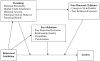
Anxiety disorders are prevalent throughout childhood and adolescence. As such, identifying the factors and mechanisms that precede, maintain, or exacerbate anxiety disorders is essential for the development of empirically based prevention and intervention programs. The current review focuses on child temperament (i.e., behavioral inhibition) and the child's environment, including parenting, childcare, and peer relationships, as these factors have been linked to internalizing problems and anxiety diagnoses. Research programs are needed that examine the associations between the environment and anxiety in temperamentally at-risk populations. In order to be successful, early intervention and prevention programs require a more detailed analysis of the interplay between various environmental contexts, both distal and proximal to the child, and the child's temperamental reactivity to novelty and threat. Furthermore, conducting these investigations across multiple levels of analysis in large-scale, longitudinal samples would be an important addition to the literature on the developmental psychopathology of anxiety.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2000. text revision.
-
- American Psychological Association. APA Dictionary of Psychology. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association; 2007.
-
- Arcus D, McCartney K. When baby makes four: Family influences in the stability of behavioral inhibition. In: Resnick JS, editor. Perspectives on behavioral inhibition. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press; 1989. pp. 197–218.
-
- Baron RM, Kenny DA. The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1986;51:1173–1182. - PubMed
-
- Barrett PM, Dadds MR, Rapee RM. Family treatment of childhood anxiety: a controlled trial. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1996;64:333–342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials