Hypoxia stimulates hepatocyte epithelial to mesenchymal transition by hypoxia-inducible factor and transforming growth factor-beta-dependent mechanisms
- PMID: 20158611
- PMCID: PMC3111074
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2010.02205.x
Hypoxia stimulates hepatocyte epithelial to mesenchymal transition by hypoxia-inducible factor and transforming growth factor-beta-dependent mechanisms
Abstract
Background/aims: During development of liver fibrosis, an important source of myofibroblasts is hepatocytes, which differentiate into myofibroblasts by epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT). In epithelial tumours and kidney fibrosis, hypoxia, through activation of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs), is an important stimulus of EMT. Our recent studies demonstrated that HIF-1alpha is important for the development of liver fibrosis. Accordingly, the hypothesis was tested that hypoxia stimulates hepatocyte EMT by a HIF-dependent mechanism.
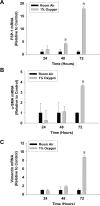
Methods: Primary mouse hepatocytes were exposed to room air or 1% oxygen and EMT evaluated. In addition, bile duct ligations (BDLs) were performed in control and HIF-1alpha-deficient mice and EMT quantified.
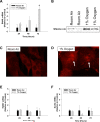
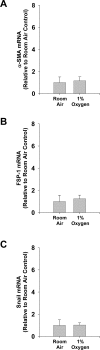
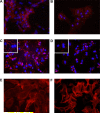
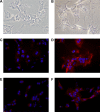
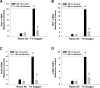
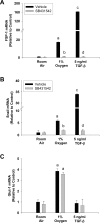
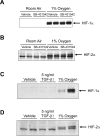
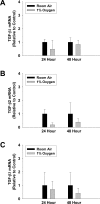
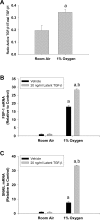
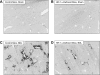
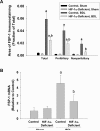
Results: Exposure of hepatocytes to 1% oxygen increased expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin, vimentin, Snail and fibroblast-specific protein-1 (FSP-1). Levels of E-cadherin and zona occludens-1 were decreased. Upregulation of FSP-1 and Snail by hypoxia was completely prevented in HIF-1beta-deficient hepatocytes and by pretreatment with SB431542, a transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) receptor inhibitor. HIFs promoted TGF-beta-dependent EMT by stimulating activation of latent TGF-beta1. To determine whether HIF-1alpha contributes to EMT in the liver during the development of fibrosis, control and HIF-1alpha-deficient mice were subjected to BDL. FSP-1 was increased to a greater extent in the livers of control mice when compared with HIF-1alpha-deficient mice.
Conclusions: Results from these studies demonstrate that hypoxia stimulates hepatocyte EMT by a HIF and TGF-beta-dependent mechanism. Furthermore, these studies suggest that HIF-1alpha is important for EMT in the liver during the development of fibrosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl-hydroxylase-2 mediates transforming growth factor beta 1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal tubular cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jun;1833(6):1454-62. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.02.029. Epub 2013 Mar 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23466866 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-induced alveolar epithelial-mesenchymal transition requires mitochondrial ROS and hypoxia-inducible factor 1.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009 Dec;297(6):L1120-30. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00007.2009. Epub 2009 Oct 2. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19801454 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia upregulates Cxcl12 in hepatocytes by a complex mechanism involving hypoxia-inducible factors and transforming growth factor-β.Cytokine. 2020 Mar;127:154986. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2020.154986. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Cytokine. 2020. PMID: 31951966 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions in the liver.Hepatology. 2009 Dec;50(6):2007-13. doi: 10.1002/hep.23196. Hepatology. 2009. PMID: 19824076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibrosis and cancer: do myofibroblasts come also from epithelial cells via EMT?J Cell Biochem. 2007 Jul 1;101(4):830-9. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21186. J Cell Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17211838 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biliary fibrosis is an important but neglected pathological feature in hepatobiliary disorders: from molecular mechanisms to clinical implications.Med Rev (2021). 2024 Jul 1;4(4):326-365. doi: 10.1515/mr-2024-0029. eCollection 2024 Aug. Med Rev (2021). 2024. PMID: 39135601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of a Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitor (L-NAME) on Ischemia⁻Reperfusion Injury of Cholestatic Livers by Pringle Maneuver and Liver Resection after Bile Duct Ligation in Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 29;20(9):2114. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092114. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31035686 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-fibrotic Effects of Synthetic Oligodeoxynucleotide for TGF-β1 and Smad in an Animal Model of Liver Cirrhosis.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017 Sep 15;8:250-263. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2017.06.022. Epub 2017 Jul 3. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017. PMID: 28918026 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of MicroRNA-19b predicts good prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma presenting with vascular invasion or multifocal disease.BMC Cancer. 2015 Oct 9;15:665. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1671-5. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26453548 Free PMC article.
-
Asparagus Polysaccharide inhibits the Hypoxia-induced migration, invasion and angiogenesis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells partly through regulating HIF1α/VEGF expression via MAPK and PI3K signaling pathway.J Cancer. 2021 May 10;12(13):3920-3929. doi: 10.7150/jca.51407. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34093799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rygiel KA, Robertson H, Marshall HL, Pekalski M, Zhao L, Booth TA, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition contributes to portal tract fibrogenesis during human chronic liver disease. Lab Invest. 2008;88(2):112–23. - PubMed
-
- Zeisberg M, Yang C, Martino M, Duncan MB, Rieder F, Tanjore H, et al. Fibroblasts derive from hepatocytes in liver fibrosis via epithelial to mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(32):23337–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

