Adult case of partial trisomy 9q
- PMID: 20158889
- PMCID: PMC2850894
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2350-11-26
Adult case of partial trisomy 9q
Abstract
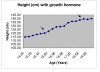
Background: Complete and partial trisomy 9 is the fourth most common chromosomal disorder. It is also associated with various congenital characteristics affecting the cranio-facial, skeletal, central nervous, gastrointestinal, cardiac and renal systems. Very few cases have been reported in adults. Partial trisomy 9q is also associated with short stature, poor growth and growth hormone deficiency. This is the first reported case of an extensive endocrinology investigation of short stature in trisomy 9q and the outcome of growth hormone treatment.
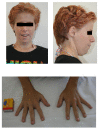
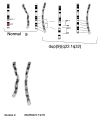
Case presentation: The case involves a 23-year-old female of pure partial trisomy 9q. The case involves a 23-year old female with pure partial trisomy 9q involving a duplication of 9q22.1 to q32, de novo, confirmed by genetic studies using fluorescene in situ hybridization (FISH) method. The diagnosis was at 6 years of age. She did not demonstrate all the congenital morphologies identified with trisomy 9q disorders especially in relation to multi-organ morphologies. There is also a degree of associated intellectual impairment. At prepuberty, she was referred for poor growth and was diagnosed with partial growth hormone deficiency. She responded very well to treatment with growth hormone and is currently living an independent life with some support.
Conclusions: Trisomy 9q is associated with short stature and failure to thrive. Growth hormone deficiency should be identified in cases of trisomy 9q and treatment offered. This is the first reported case of response to growth hormone replacement in partial trisomy 9.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of a Complex Chromosomal Rearrangement Involving a de novo Duplication of 9p and 9q and a Deletion of 9q.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2015;147(2-3):124-9. doi: 10.1159/000444138. Epub 2016 Feb 23. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2015. PMID: 26900692
-
Brief report. Adult patient presenting an interstitial (9) (q21.32q31.1) direct duplication resulting from the malsegregation of a paternal balanced insertional translocation.Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2014 Apr;100(4):294-9. doi: 10.1002/bdra.23215. Epub 2014 Mar 26. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2014. PMID: 24668944 Review.
-
Partial trisomy 9q syndrome with a de novo tandem duplication of 9q22.2-q31.1.Genet Couns. 2005;16(4):407-12. Genet Couns. 2005. PMID: 16440884
-
Partial monosomy 8q and partial trisomy 9q due to the maternal translocation t(8;9(q24.3;q34.1): a case report.Genet Couns. 2014;25(1):35-9. Genet Couns. 2014. PMID: 24783653
-
Duplication of 9q12-q33: a case report and implications for the dup(9q) syndrome.Am J Med Genet. 1993 Feb 15;45(4):456-9. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320450412. Am J Med Genet. 1993. PMID: 8465850 Review.
Cited by
-
Schilbach-Rott syndrome associated with 9q22.32q22.33 duplication, involving the PTCH1 gene.Eur J Hum Genet. 2019 Aug;27(8):1260-1266. doi: 10.1038/s41431-019-0385-6. Epub 2019 Apr 1. Eur J Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 30936464 Free PMC article.
-
When Feeding Difficulties Are due to Genetics: The Case of Familial Partial 9q Duplication.J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2015 Feb 18;3(1):2324709615574949. doi: 10.1177/2324709615574949. eCollection 2015 Jan-Mar. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2015. PMID: 26425634 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Temtamy SA, Kamel AK, Ismail S, Helmy NA, Aglan MS, El Gammal M, El Ruby M, Mohammed AM. Phenotypic and cytogenetic spectrum of 9p trisomy. Genet Couns. 2007;18:29–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

