Differential roles for the IL-9/IL-9 receptor alpha-chain pathway in systemic and oral antigen-induced anaphylaxis
- PMID: 20159257
- PMCID: PMC4259249
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.09.054
Differential roles for the IL-9/IL-9 receptor alpha-chain pathway in systemic and oral antigen-induced anaphylaxis
Abstract
Background: The cytokine IL-9 has been implicated in allergic reactions, including food allergy, but its contribution to parenteral versus oral antigen-induced anaphylaxis remains unclear.
Objectives: We sought to delineate the contribution of the IL-9/IL-9 receptor alpha-chain (IL-9R) pathway to parenteral and oral antigen-induced anaphylaxis.
Methods: Wild-type, IL-9-deficient (Il9(-/-)), and IL-9R-deficient (Il9R(-/-)) mice were subjected to passive and active parenteral and oral antigen (ovalbumin [OVA])-induced anaphylaxis. Severity of systemic anaphylaxis was gauged by decreased body temperature; intestinal anaphylaxis was assessed based on secretory diarrhea, intestinal mastocytosis, and serum murine mast cell protease 1 level. Specific immunoglobulin isotypes or immunoglobulin receptor-blocking antibodies were administered before challenge to define the role of the IgE and IgG pathways.
Results: Repeated oral antigen challenge of OVA-sensitized wild-type mice induced anaphylaxis with both systemic and intestinal involvement; both were IgE dependent and attenuated in Il9(-/-) and Il9R(-/-) mice. In contrast, parenteral OVA challenge of OVA-sensitized wild-type mice induced systemic anaphylaxis, which was independent of the IL-9/IL-9R pathway. Strikingly, the IL-9/IL-9R pathway had no role in either the IgG or IgE component of parenteral antigen-induced or anti-IgE and anti-FcgammaRII/III mAb-induced systemic anaphylaxis.
Conclusions: Parenteral antigen-induced murine systemic anaphylaxis is mediated by both IgG- and IgE-dependent pathways, and both can occur independently of IL-9/IL-9R signaling. In contrast, oral antigen-induced intestinal and systemic anaphylaxis is strictly IgE mediated and requires IL-9/IL-9R signaling. These studies indicate differential involvement of the IL-9/IL-9R pathway in systemic and oral antigen-induced anaphylaxis.
Copyright 2010 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of potential conflict of interest: F. D. Finkelman is a consultant for Abbott and Associate Editor for the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, has received research support from Abbott, and is treasurer-elect for the American Association of Immunologists. The rest of the authors have declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
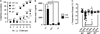
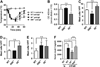
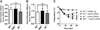
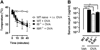
References
-
- Simons FE, Frew AJ, Ansotegui IJ, Bochner BS, Golden DB, Finkelman FD, et al. Risk assessment in anaphylaxis: current and future approaches. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;120(suppl):S2–S4. - PubMed
-
- Sicherer SH, Leung DY. Advances in allergic skin disease, anaphylaxis, and hyper-sensitivity reactions to foods, drugs, and insects. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;116:153–163. - PubMed
-
- Greenberger PA. Drug Allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117(suppl):S464–S470. - PubMed
-
- Bock SA, Munoz-Furlong A, Sampson HA. Fatalities due to anaphylactic reactions to foods. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;107:191–193. - PubMed
-
- Wang J, Sampson HA. Food anaphylaxis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2007;37:651–660. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

