Cysteinyl leukotrienes acting via granule membrane-expressed receptors elicit secretion from within cell-free human eosinophil granules
- PMID: 20159258
- PMCID: PMC2824614
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.11.029
Cysteinyl leukotrienes acting via granule membrane-expressed receptors elicit secretion from within cell-free human eosinophil granules
Abstract
Background: Cysteinyl leukotrienes (cysLTs) are recognized to act via receptors (cysLTRs) expressed on cell surface plasma membranes. Agents that block cysLT(1) receptor (cysLT(1)R) are therapeutics for allergic disorders. Eosinophils contain multiple preformed proteins stored within their intracellular granules. Cell-free eosinophil granules are present extracellularly as intact membrane-bound organelles in sites associated with eosinophil infiltration, including asthma, rhinitis, and urticaria, but have unknown functional capabilities.
Objective: We evaluated the expression of cysLTRs on eosinophil granule membranes and their functional roles in eliciting protein secretion from within eosinophil granules.
Methods: We studied secretory responses of human eosinophil granules isolated by subcellular fractionation. Granules were stimulated with cysLTs, and eosinophil cationic protein and cytokines were measured in the supernatants. Receptor expression on granule membranes and eosinophils was evaluated by flow cytometry and Western blot.
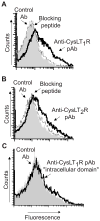
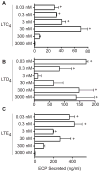
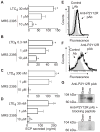
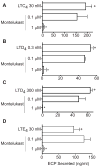
Results: We report that receptors for cysLTs, cysLT(1)R, cysLT(2) receptor, and the purinergic P2Y12 receptor, are expressed on eosinophil granule membranes. Leukotriene (LT) C(4) and extracellularly generated LTD(4) and LTE(4) stimulated isolated eosinophil granules to secrete eosinophil cationic protein. MRS 2395, a P2Y12 receptor antagonist, inhibited cysLT-induced eosinophil cationic protein release. Montelukast, likely not solely as an inhibitor of cysLT(1)R, inhibited eosinophil cationic protein release elicited by LTC(4) and LTD(4) as well as by LTE(4).
Conclusion: These studies identify previously unrecognized sites of localization, the membranes of intracellular eosinophil granule organelles, and function for cysLT-responsive receptors that mediate cysteinyl leukotriene-stimulated secretion from within eosinophil granules, including those present extracellularly.
Copyright 2010 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Intelligent granules: are eosinophil crystalloid granules inimitable?J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010 Jul;126(1):28-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.04.008. Epub 2010 Jun 9. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20538325 No abstract available.
References
-
- Peters-Golden M, Henderson WR., Jr Leukotrienes. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:1841–54. - PubMed
-
- Lynch KR, O’Neill GP, Liu Q, Im DS, Sawyer N, Metters KM, et al. Characterization of the human cysteinyl leukotriene CysLT1 receptor. Nature. 1999;399:789–93. - PubMed
-
- Heise CE, O’Dowd BF, Figueroa DJ, Sawyer N, Nguyen T, Im DS, et al. Characterization of the human cysteinyl leukotriene 2 receptor. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:30531–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

