Genetics of addictions
- PMID: 20159342
- PMCID: PMC3047504
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psc.2009.10.003
Genetics of addictions
Abstract
Addictions include a group of common, heritable psychiatric illnesses that have multiple psychiatric and medical comorbidities. Robust genetic associations have been found for alcohol dependence, nicotine dependence, and cocaine dependence. Common genetic associations have been found between alcohol dependence and aerodigestive cancers and between nicotine dependence and lung disease. These associations highlight the importance of understanding the genetics of substance dependence in the context of its multiple medical and psychiatric comorbidities.
Copyright 2010. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures



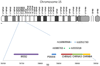
Republished in
-
Genetics of addictions.Clin Lab Med. 2010 Dec;30(4):847-64. doi: 10.1016/j.cll.2010.07.005. Clin Lab Med. 2010. PMID: 20832656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-IV-TR. 4th edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2000. Task Force on DSM-IV.
-
- Grant BF, Hasin DS, Chou SP, et al. Nicotine dependence and psychiatric disorders in the United States: results from the national epidemiologic survey on alcohol and related conditions. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2004;61(11):1107–1115. - PubMed
-
- Regier DA, Farmer ME, Rae DS, et al. Comorbidity of mental disorders with alcohol and other drug abuse. Results from the Epidemiologic Catchment Area (ECA) Study. JAMA. 1990;264(19):2511–2518. - PubMed
-
- Clark RE, Samnaliev M, McGovern MP. Treatment for co-occurring mental and substance use disorders in five state Medicaid programs. Psychiatr Serv. 2007;58(7):942–948. - PubMed
-
- Lasser K, Boyd JW, Woolhandler S, et al. Smoking and mental illness: a population-based prevalence study. JAMA. 2000;284(20):2606–2610. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

