Sonic hedgehog signaling confers ventral telencephalic progenitors with distinct cortical interneuron fates
- PMID: 20159447
- PMCID: PMC2868511
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.01.004
Sonic hedgehog signaling confers ventral telencephalic progenitors with distinct cortical interneuron fates
Abstract
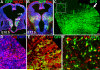
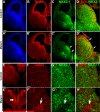
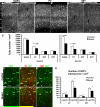
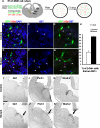
Interneurons in the cerebral cortex regulate cortical functions through the actions of distinct subgroups that express parvalbumin, somatostatin, or calretinin. The genesis of the first two subgroups requires the expression of NKX2.1, which is maintained by SHH signaling during neurogenesis. In this paper, we report that mosaic elimination in the medial ganglionic eminence (MGE) of Smo, a key effector of SHH signaling, reveals that MGE progenitors retain a remarkable degree of plasticity during the neurogenic period. SHH signaling prevents the upregulation of GSX2 and conversion of some MGE progenitors to a caudal ganglionic eminence-like, bipolar calretinin-expressing cell fate that is promoted by GSX2. In addition, a higher level of SHH signaling promotes the generation of the somatostatin-expressing interneuron at the expense of parvalbumin-expressing subgroup. These results indicate that cortical interneuron diversity, a major determinant of cortical function, is critically influenced by differential levels of SHH signaling within the ventral telencephalon.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Duration of culture and sonic hedgehog signaling differentially specify PV versus SST cortical interneuron fates from embryonic stem cells.Development. 2015 Apr 1;142(7):1267-78. doi: 10.1242/dev.111526. Development. 2015. PMID: 25804737 Free PMC article.
-
Sonic hedgehog maintains the identity of cortical interneuron progenitors in the ventral telencephalon.Development. 2005 Nov;132(22):4987-98. doi: 10.1242/dev.02090. Epub 2005 Oct 12. Development. 2005. PMID: 16221724
-
Spatial and temporal bias in the mitotic origins of somatostatin- and parvalbumin-expressing interneuron subgroups and the chandelier subtype in the medial ganglionic eminence.Cereb Cortex. 2012 Apr;22(4):820-7. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhr148. Epub 2011 Jun 21. Cereb Cortex. 2012. PMID: 21693785 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Regulation of Cortical Interneuron Development.In: Noebels JL, Avoli M, Rogawski MA, Vezzani A, Delgado-Escueta AV, editors. Jasper's Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies. 5th edition. New York: Oxford University Press; 2024. Chapter 47. In: Noebels JL, Avoli M, Rogawski MA, Vezzani A, Delgado-Escueta AV, editors. Jasper's Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies. 5th edition. New York: Oxford University Press; 2024. Chapter 47. PMID: 39637134 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Cortical interneuron fate determination: diverse sources for distinct subtypes?Cereb Cortex. 2003 Jun;13(6):670-6. doi: 10.1093/cercor/13.6.670. Cereb Cortex. 2003. PMID: 12764043 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Mechanisms Underlying Cortical Evolution in Mammals.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Feb 15;9:591017. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.591017. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33659245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Local Thyroid Hormone Action in Brain Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 2;24(15):12352. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512352. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuronal Transplantation for Alzheimer's Disease and Prospects for Generating Exogenic Neurons as a Source of Cells for Implantation.Cell Transplant. 2023 Jan-Dec;32:9636897231164712. doi: 10.1177/09636897231164712. Cell Transplant. 2023. PMID: 37219048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ventromedian forebrain dysgenesis follows early prenatal ethanol exposure in mice.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2011 Mar-Apr;33(2):231-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2010.11.001. Epub 2010 Nov 11. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2011. PMID: 21074610 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of SoxB1-dependent Sonic hedgehog expression in the hypothalamus causes septo-optic dysplasia.Dev Cell. 2012 Mar 13;22(3):585-96. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.12.023. Dev Cell. 2012. PMID: 22421044 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn S, Joyner AL. Dynamic changes in the response of cells to positive hedgehog signaling during mouse limb patterning. Cell. 2004;118:505–516. - PubMed
-
- Anderson SA, Marin O, Horn C, Jennings K, Rubenstein JL. Distinct cortical migrations from the medial and lateral ganglionic eminences. Development. 2001;128:353–363. - PubMed
-
- Butt SJ, Fuccillo M, Nery S, Noctor S, Kriegstein A, Corbin JG, Fishell G. The temporal and spatial origins of cortical interneurons predict their physiological subtype. Neuron. 2005;48:591–604. - PubMed
-
- Cavanagh ME, Parnavelas JG. Development of vasoactive-intestinal-polypeptide-immunoreactive neurons in the rat occipital cortex: a combined immunohistochemical-autoradiographic study. J Comp Neurol. 1989;284:637–645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

