Microbial colonization drives expansion of IL-1 receptor 1-expressing and IL-17-producing gamma/delta T cells
- PMID: 20159619
- PMCID: PMC4048034
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2010.01.005
Microbial colonization drives expansion of IL-1 receptor 1-expressing and IL-17-producing gamma/delta T cells
Abstract
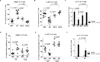
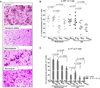
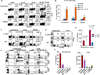
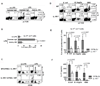
IL-17 cytokine production by the Th17 T cell subset is regulated by intestinal commmensals. We show that microbial colonization also regulates innate IL-17 production. A population of CD62L(-) gamma/delta T cells, in particular a lineage expressing the IL-1 receptor 1 (IL-1R1), can be quickly activated by microbes to produce IL-17. Antibiotic treatment and monocolonization of mice suggest that specific commensals-but not metronidazole-sensitive anaerobes like Bacteroides species-are required for maintaining IL-1R1(+) gamma/delta T cells. Signaling through the guanine nucleotide exchange factor VAV1, but not through Toll-like receptors or antigen presentation pathways, is essential for inducing IL-1R1(+) gamma/delta T cells. Furthermore, IL-1R1(+) gamma/delta T cells are a potential source of IL-17 that can be activated by IL-23 and IL-1 in both infectious and noninfectious settings in vitro and in vivo. Thus, commensals orchestrate the expansion of phenotypically distinct gammadelta T cells, and innate immunity is a three-way interaction between host, pathogens, and microbiota.
2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Adachi O, Kawai T, Takeda K, Matsumoto M, Tsutsui H, Sakagami M, Nakanishi K, Akira S. Targeted disruption of the MyD88 gene results in loss of IL-1- and IL-18-mediated function. Immunity. 1998;9:143–150. - PubMed
-
- Akira S. Toll-like receptor signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278(40):38105–38108. - PubMed
-
- Atarashi K, Nishimura J, Shima T, Umesaki Y, Yamamoto M, Onoue M, Yagita H, Ishii N, Evans R, Honda K, Takeda K. ATP drives lamina propria T(H)17 cell differentiation. Nature. 2008;455(7214):808–812. - PubMed
-
- Chao CC, Jensen R, Dailey MO. Mechanisms of L-selectin regulation by activated T cells. J. Immunol. 1997;159(4):1686–1694. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

