Free-breathing diffusion-weighted single-shot echo-planar MR imaging using parallel imaging (GRAPPA 2) and high b value for the detection of primary rectal adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 20159662
- PMCID: PMC2842173
- DOI: 10.1102/1470-7330.2010.0011
Free-breathing diffusion-weighted single-shot echo-planar MR imaging using parallel imaging (GRAPPA 2) and high b value for the detection of primary rectal adenocarcinoma
Abstract
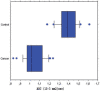
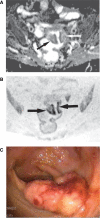
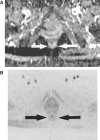
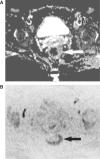
Our objective was to determine the diagnostic accuracy of a free-breathing diffusion-weighted single-shot echo-planar magnetic resonance imaging (FBDW-SSEPI) technique with parallel imaging and high diffusion factor value (b = 1000 s/mm2) in the detection of primary rectal adenocarcinomas. Thirty-one patients (14M and 17F; mean age 67 years) with histopathologically proven primary rectal adenocarcinomas and 31 patients without rectal malignancies (14M and 17F; mean age 63.6 years) were examined with FBDW-SSEPI (repetition time (TR/echo time (TE) 3900/91 ms, gradient strength 45 mT/m, acquisition time 2 min) at 1.5 T using generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA, acceleration factor 2) and a b value of 1000 s/mm2. Apparent diffusion coefficients (ADCs) of rectal adenocarcinomas and normal rectal wall were measured. FBDW-SSEPI images were evaluated for tumour detection by 2 readers. Sensitivity, specificity, accuracy and Youden score for rectal adenocarcinoma detection were calculated with their 95% confidence intervals (CI) for ADC value measurement and visual image analysis. Rectal adenocarcinomas had significantly lower ADCs (mean 1.036 x 10(-3)+/- 0.107 x 10(-3) mm2/s; median 1.015 x 10(-3) mm2/s; range (0.827-1.239) x 10(-3) mm2/s) compared with the rectal wall of control subjects (mean 1.387 x 10(-3)+/- 0.106 x 10(-3) mm2/s; median 1.385 x 10(-3) mm2/s; range (1.176-1.612) x 10(-3) mm2/s) (p < 0.0001). Using a threshold value < or = 1.240 x 10(-3) mm2/s, all rectal adenocarcinomas were correctly categorized and 100% sensitivity (31/31; 95% CI 95-100%), 94% specificity (31/33; 95% CI 88-100%), 97% accuracy (60/62; 95% CI 92-100%) and Youden index 0.94 were obtained for the diagnosis of rectal adenocarcinoma. FBDW-SSEPI image analysis allowed depiction of all rectal adenocarcinomas but resulted in 2 false-positive findings, yielding 100% sensitivity (31/31; 95% CI 95-100%), 94% specificity (31/33; 95% CI 88-100%), 97% accuracy (60/62; 95% CI 92-100%) and Youden index 0.94 for the diagnosis of primary rectal adenocarcinoma. We can conclude that FBDW-SSEPI using parallel imaging and high b value may be helpful in the detection of primary rectal adenocarcinomas.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Solid bone tumors of the spine: Diagnostic performance of apparent diffusion coefficient measured using diffusion-weighted MRI using histology as a reference standard.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018 Apr;47(4):1034-1042. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25826. Epub 2017 Jul 29. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018. PMID: 28755383
-
Comparison of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in the Human Brain Using Readout-Segmented EPI and PROPELLER Turbo Spin Echo With Single-Shot EPI at 7 T MRI.Invest Radiol. 2016 Jul;51(7):435-9. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000248. Invest Radiol. 2016. PMID: 26807895
-
ADC measurement of abdominal organs and lesions using parallel imaging technique.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006 Dec;187(6):1521-30. doi: 10.2214/AJR.05.0778. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006. PMID: 17114546
-
Diffusion-weighted MRI in evaluating liver fibrosis: a feasibility study in cirrhotic patients.Radiol Med. 2007 Apr;112(3):394-408. doi: 10.1007/s11547-007-0149-1. Epub 2007 Apr 20. Radiol Med. 2007. PMID: 17440695 English, Italian.
-
The clinical value of applying diffusion-weighted imaging combined with T2-weighted imaging to assess diagnostic performance of muscularis propria invasion in mid-to-high rectal cancer.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025 Feb;50(2):598-607. doi: 10.1007/s00261-024-04536-w. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2025. PMID: 39207517 Review.
Cited by
-
The Multipurpose Usage of Diffusion-Weighted MRI in Rectal Cancer.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Dec 13;59(12):2162. doi: 10.3390/medicina59122162. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 38138265 Free PMC article.
-
Multiparametric MRI in rectal cancer.Diagn Interv Radiol. 2019 May;25(3):175-182. doi: 10.5152/dir.2019.18189. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2019. PMID: 31063142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated slice-specific dynamic shimming diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) for rectal Cancer detection and characterization.Cancer Imaging. 2021 Apr 7;21(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s40644-021-00403-9. Cancer Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33827704 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted MRI of Rectal Cancer Using a Residual Convolutional Network.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Mar 14;10(3):359. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10030359. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36978750 Free PMC article.
-
Noninvasive Biomarkers of Colorectal Cancer: Role in Diagnosis and Personalised Treatment Perspectives.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2018 Jun 13;2018:2397863. doi: 10.1155/2018/2397863. eCollection 2018. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2018. PMID: 30008744 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ichikawa T, Haradome H, Hachiya J, Nitatori T, Araki T. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging with single-shot echo-planar imaging in the upper abdomen: preliminary clinical experience in 61 patients. Abdom Imaging. 1999;24:456–61. doi:10.1007/s002619900539. PMid:10475927. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ichikawa T, Ertuk SM, Motosugi U, et al. High-b-value diffusion-weighted MRI in colorectal cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006;187:181–4. doi:10.2214/AJR.05.1005. PMid:16794174. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ichikawa T, Haradome H, Hachiya J, Nitatori T, Araki T. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging with a single-shot echoplanar sequence: detection and characterization of focal hepatic lesions. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998;170:397–402. - PubMed
-
- Taouli B, Martin AJ, Qayyum A, et al. Parallel imaging and diffusion tensor imaging for diffusion-weighted MRI of the liver: preliminary experience in healthy volunteers. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;183:677–80. - PubMed
-
- Rao SX, Zeng MS, Chen CZ, et al. The value of diffusion-weighted imaging in combination with T2-weighted imaging for rectal cancer detection. Eur J Radiol. 2008;65:299–303. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2007.04.001. PMid:17498902. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
