Linking endoplasmic reticulum stress to cell death in hepatocytes: roles of C/EBP homologous protein and chemical chaperones in palmitate-mediated cell death
- PMID: 20159858
- PMCID: PMC2867372
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00642.2009
Linking endoplasmic reticulum stress to cell death in hepatocytes: roles of C/EBP homologous protein and chemical chaperones in palmitate-mediated cell death
Abstract
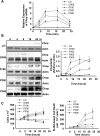
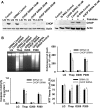
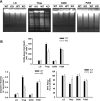
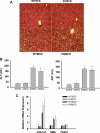
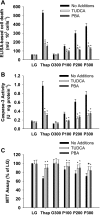
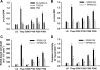
Prolonged endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and activation of the unfolded protein response (UPR) have been linked to apoptosis via several mechanisms, including increased expression of C/EBP homologous protein (Chop). Increased long-chain fatty acids, in particular saturated fatty acids, induce ER stress, Chop expression, and apoptosis in liver cells. The first aim of the present study was to determine the role of Chop in lipid-induced hepatocyte cell death and liver injury induced by a methionine-choline-deficient diet. Albumin-bound palmitate increased Chop gene and protein expression in a dose-dependent fashion in H4IIE liver cells. siRNA-mediated silencing of Chop in H4IIE liver cells reduced thapsigargin-mediated cell death by approximately 40% and delayed palmitate-mediated cell death, but only at high concentrations of palmitate (400-500 microM). Similar results were observed in primary hepatocytes isolated from Chop-knockout mice. Indices of liver injury were also not reduced in Chop-knockout mice provided a methionine-choline-deficient diet. To ascertain whether ER stress was linked to palmitate-induced cell death, primary hepatocytes were incubated in the absence or presence of the chemical chaperones taurine-conjugated ursodeoxycholic acid or 4-phenylbutyric acid. The presence of either of these chemical chaperones protected liver cells from palmitate-mediated ER stress and cell death, in part, via inhibition of JNK activation. These data suggest that ER stress is linked to palmitate-mediated cell death via mechanisms that include JNK activation.
Figures
References
-
- Abdelmalek MF, Diehl A. Mechanisms underlying nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Drug Discov Today Dis Mech 3: 479–488, 2006
-
- Barreyro FJ, Kobayashi S, Bronk SF, Werneburg NW, Malhi H, Gores GJ. Transcriptional regulation of Bim by FoxO3A mediates hepatocyte lipoapoptosis. J Biol Chem 282: 27141–27154, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

