A new antidiabetic compound attenuates inflammation and insulin resistance in Zucker diabetic fatty rats
- PMID: 20159859
- PMCID: PMC2867370
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00668.2009
A new antidiabetic compound attenuates inflammation and insulin resistance in Zucker diabetic fatty rats
Abstract
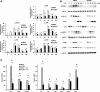
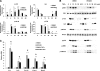
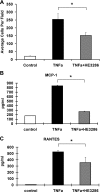
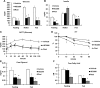
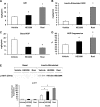
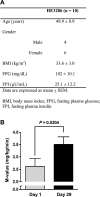
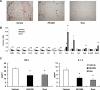
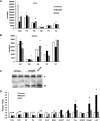
Tissue macrophage inflammatory pathways contribute to obesity-associated insulin resistance. Here, we have examined the efficacy and mechanisms of action of a novel anti-inflammatory compound (HE3286) in vitro and in vivo. In primary murine macrophages, HE3286 attenuates LPS- and TNFalpha-stimulated inflammation. In Zucker diabetic fatty rats, inflammatory cytokine/chemokine expression was downregulated in liver and adipose tissue by HE3286 treatment, as was macrophage infiltration into adipose tissue. In line with reduced inflammation, HE3286 treatment normalized fasting and fed glucose levels, improved glucose tolerance, and enhanced skeletal muscle and liver insulin sensitivity, as assessed by hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp studies. In phase 2 clinical trials, HE3286 treatment led to an enhancement in insulin sensitivity in humans. Gluconeogenic capacity was also reduced by HE3286 treatment, as evidenced by a reduced glycemic response during pyruvate tolerance tests and decreased basal hepatic glucose production (HGP) rates. Since serum levels of gluconeogenic substrates were decreased by HE3286, it indicates that the reduction of both intrinsic gluconeogenic capacity and substrate availability contributes to the decrease in HGP. Lipidomic analysis revealed that HE3286 treatment reduced liver cholesterol and triglyceride content, leading to a feedback elevation of LDL receptor and HMG-CoA reductase expression. Accordingly, HE3286 treatment markedly decreased total serum cholesterol. In conclusion, HE3286 is a novel anti-inflammatory compound, which displays both glucose-lowering and cholesterol-lowering effects.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A synthetic anti-inflammatory sterol improves insulin sensitivity in insulin-resistant obese impaired glucose tolerance subjects.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2013 Sep;21(9):E343-9. doi: 10.1002/oby.20207. Epub 2013 May 13. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2013. PMID: 23670958 Clinical Trial.
-
Amelioration of glucose intolerance by the synthetic androstene HE3286: link to inflammatory pathways.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010 Apr;333(1):70-80. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.161182. Epub 2010 Jan 12. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010. PMID: 20068030
-
Reversal of inflammation-induced impairment of glucose uptake in adipocytes by direct effect of CB1 antagonism on adipose tissue macrophages.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2010 Dec;18(12):2247-54. doi: 10.1038/oby.2010.81. Epub 2010 Apr 8. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2010. PMID: 20379144
-
The messenger RNA profiles in liver, hypothalamus, white adipose tissue, and skeletal muscle of female Zucker diabetic fatty rats after topiramate treatment.Metabolism. 2006 Oct;55(10):1411-9. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2006.06.013. Metabolism. 2006. PMID: 16979414
-
Adipose tissue macrophages in remote modulation of hepatic glucose production.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 24;13:998947. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.998947. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36091076 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
17α-Ethynyl-androst-5-ene-3β,7β,17β-triol (HE3286) Is Neuroprotective and Reduces Motor Impairment and Neuroinflammation in a Murine MPTP Model of Parkinson's Disease.Parkinsons Dis. 2012;2012:969418. doi: 10.1155/2012/969418. Epub 2012 Sep 26. Parkinsons Dis. 2012. PMID: 23050197 Free PMC article.
-
Artemisia dracunculus L. extract ameliorates insulin sensitivity by attenuating inflammatory signalling in human skeletal muscle culture.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014 Aug;16(8):728-38. doi: 10.1111/dom.12274. Epub 2014 Mar 10. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014. PMID: 24521217 Free PMC article.
-
Studies of the pharmacology of 17α-ethynyl-androst-5-ene-3β,7β,17β-triol, a synthetic anti-inflammatory androstene.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2011;4(2):119-35. Epub 2011 Apr 23. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2011. PMID: 21686136 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between extracellular vesicles and microbiome in human diseases: New therapeutic opportunities.Imeta. 2023 Feb 6;2(2):e86. doi: 10.1002/imt2.86. eCollection 2023 May. Imeta. 2023. PMID: 38868436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HE3286, an oral synthetic steroid, treats lung inflammation in mice without immune suppression.J Inflamm (Lond). 2010 Oct 30;7:52. doi: 10.1186/1476-9255-7-52. J Inflamm (Lond). 2010. PMID: 21034489 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdul-Ghani MA, Matsuda M, Balas B, DeFronzo RA. Muscle and liver insulin resistance indexes derived from the oral glucose tolerance test. Diabetes Care 30: 89–94, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Arkan MC, Hevener AL, Greten FR, Maeda S, Li ZW, Long JM, Wynshaw-Boris A, Poli G, Olefsky J, Karin M. IKK-beta links inflammation to obesity-induced insulin resistance. Nat Med 11: 191–198, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Auci D, Kaler L, Subramanian S, Huang Y, Frincke J, Reading C, Offner H. A new orally bioavailable synthetic androstene inhibits collagen-induced arthritis in the mouse: androstene hormones as regulators of regulatory T cells. Ann NY Acad Sci 1110: 630–640, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Basu R, Dalla Man C, Campioni M, Basu A, Nair KS, Jensen MD, Khosla S, Klee G, Toffolo G, Cobelli C, Rizza RA. Two years of treatment with dehydroepiandrosterone does not improve insulin secretion, insulin action, or postprandial glucose turnover in elderly men or women. Diabetes 56: 753–766, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

