Risk of severe outcomes among patients admitted to hospital with pandemic (H1N1) influenza
- PMID: 20159893
- PMCID: PMC2831689
- DOI: 10.1503/cmaj.091823
Risk of severe outcomes among patients admitted to hospital with pandemic (H1N1) influenza
Abstract
Background: We describe the disease characteristics and outcomes, including risk factors for admission to intensive care unit (ICU) and death, of all patients in Canada admitted to hospital with pandemic (H1N1) influenza during the first five months of the pandemic.
Methods: We obtained data for all patients admitted to hospital with laboratory-confirmed pandemic (H1N1) influenza reported to the Public Health Agency of Canada from Apr. 26 to Sept. 26, 2009. We compared inpatients who had nonsevere disease with those who had severe disease, as indicated by admission to ICU or death.
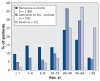
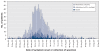
Results: A total of 1479 patients were admitted to hospital with confirmed pandemic (H1N1) influenza during the study period. Of these, 1171 (79.2%) did not have a severe outcome, 236 (16.0%) were admitted to ICU and survived, and 72 (4.9%) died. The median age was 23 years for all of the patients, 18 years for those with a nonsevere outcome, 34 years for those admitted to ICU who survived and 51 years for those who died. The risk of a severe outcome was elevated among those who had an underlying medical condition and those 20 years of age and older. A delay of one day in the median time between the onset of symptoms and admission to hospital increased the risk of death by 5.5%. The risk of a severe outcome remained relatively constant over the five-month period.
Interpretation: The population-based incidence of admission to hospital with laboratory-confirmed pandemic (H1N1) influenza was low in the first five months of the pandemic in Canada. The risk of a severe outcome was associated with the presence of one or more underlying medical conditions, age of 20 years or more and a delay in hospital admission.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global influenza programme: global surveillance during an influenza pandemic, version 1. Geneva (Switzerland): The Organization; 2009. [(accessed 2009 Sept. 1)]. Available: www.who.int/csr/disease/swineflu/global_pandemic_influenza_surveilance_a....
-
- Public Health Agency of Canada. FluWatch: Definitions for the 2009–2010 season. Ottawa (ON): The Agency; 2009. [(accessed 2009 Nov. 25)]. Available: www.phac-aspc.gc.ca/fluwatch/09-10/def09-10-eng.php.
-
- National Advisory Committee on Immunization (NACI) Statement on influenza vaccination for the 2008–2009 season. [(accessed 2009 Nov. 1)];Can Commun Dis Rep. 2008 34(ACS-3):1–46. Available: www.phac-aspc.gc.ca/publicat/ccdr-rmtc/08vol34/acs-3/index-eng.php. - PubMed
-
- Use of influenza A (H1N1) 2009 monovalent vaccine, recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), 2009. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2009;58(RR-10):1–8. - PubMed
-
- Age and sex highlight tables, 2006 census. Ottawa (ON): Statistics Canada; 2009. [(accessed 2009 Sept. 25)]. Available: www12.statcan.gc.ca/english/census06/data/highlights/agesex/index.cfm.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
