Arsenic trioxide-dependent activation of thousand-and-one amino acid kinase 2 and transforming growth factor-beta-activated kinase 1
- PMID: 20159944
- PMCID: PMC2872974
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.109.061507
Arsenic trioxide-dependent activation of thousand-and-one amino acid kinase 2 and transforming growth factor-beta-activated kinase 1
Abstract
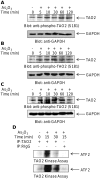
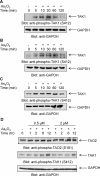
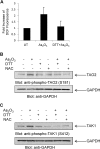
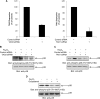
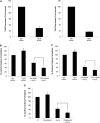
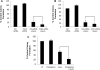
Arsenic trioxide (As(2)O(3)) has potent antileukemic properties in vitro and in vivo, but the mechanisms by which it generates its effects on target leukemic cells are not well understood. Understanding cellular mechanisms and pathways that are activated in leukemic cells to control the generation of As(2)O(3) responses should have important implications in the development of novel approaches using As(2)O(3) for the treatment of leukemias. In this study, we used immunoblotting and immune complex kinase assays to provide evidence that the kinases thousand-and-one amino acid kinase 2 (TAO2) and transforming growth factor-beta-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) are rapidly activated in response to treatment of acute leukemia cells with As(2)O(3). Such activation occurs after the generation of reactive oxygen species and regulates downstream engagement of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Our studies demonstrate that siRNA-mediated knockdown of TAO2 or TAK1 or pharmacological inhibition of TAK1 enhances the suppressive effects of As(2)O(3) on KT-1-derived leukemic progenitor colony formation and on primary leukemic progenitors from patients with acute myelogenous leukemia. These results indicate key negative-feedback regulatory roles for these kinases in the generation of the antileukemic effects of As(2)O(3). Thus, molecular or pharmacological targeting of these kinases may provide a novel approach to enhance the generation of arsenic-dependent antileukemic responses.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulatory effects of mammalian target of rapamycin-mediated signals in the generation of arsenic trioxide responses.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jan 25;283(4):1992-2001. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705227200. Epub 2007 Nov 29. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18048359
-
Role of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in the generation of arsenic trioxide-dependent cellular responses.Cancer Res. 2006 Jul 1;66(13):6763-71. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3699. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16818652
-
Activation of Rac1 and the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in response to arsenic trioxide.J Biol Chem. 2002 Nov 22;277(47):44988-95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M207176200. Epub 2002 Sep 17. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12239215
-
The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway and its role in interferon signaling.Pharmacol Ther. 2003 May;98(2):129-42. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7258(03)00016-0. Pharmacol Ther. 2003. PMID: 12725866 Review.
-
Arsenic-induced apoptosis in malignant cells in vitro.Leuk Lymphoma. 2000 Mar;37(1-2):53-63. doi: 10.3109/10428190009057628. Leuk Lymphoma. 2000. PMID: 10721769 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of the kinase RSK1 by arsenic trioxide and generation of antileukemic responses.Cancer Biol Ther. 2013 May;14(5):411-6. doi: 10.4161/cbt.23760. Epub 2013 Feb 1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23377826 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory effects of sestrin 3 (SESN3) in BCR-ABL expressing cells.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 18;8(11):e78780. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078780. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24260131 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol enhances the suppressive effects of arsenic trioxide on primitive leukemic progenitors.Cancer Biol Ther. 2014 Apr;15(4):473-8. doi: 10.4161/cbt.27824. Epub 2014 Feb 4. Cancer Biol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24496081 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Response of Glioma Stem Cells to Arsenic Trioxide Therapy Is Regulated by MNK1 and mRNA Translation.Mol Cancer Res. 2018 Jan;16(1):32-46. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-17-0397. Epub 2017 Oct 17. Mol Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29042487 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal TAOK2 contributes to neuropathic pain via cGAS-STING activation in rats.iScience. 2023 Aug 30;26(10):107792. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107792. eCollection 2023 Oct 20. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37720090 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altman JK, Yoon P, Katsoulidis E, Kroczynska B, Sassano A, Redig AJ, Glaser H, Jordan A, Tallman MS, Hay N, et al. (2008) Regulatory effects of mammalian target of rapamycin-mediated signals in the generation of arsenic trioxide responses. J Biol Chem 283:1992–2001 - PubMed
-
- Chen Z, Chen GQ, Shen ZX, Sun GL, Tong JH, Wang ZY, Chen SJ. (2002) Expanding the use of arsenic trioxide: leukemias and beyond. Semin Hematol 39:22–26 - PubMed
-
- Chen Z, Cobb MH. (2001) Regulation of stress-responsive mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways by TAO2. J Biol Chem 276:16070–16075 - PubMed
-
- Chen Z, Hutchison M, Cobb MH. (1999) Isolation of the protein kinase TAO2 and identification of its mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase binding domain. J Biol Chem 274:28803–28807 - PubMed
-
- Chen Z, Raman M, Chen L, Lee SF, Gilman AG, Cobb MH. (2003) TAO (thousand-and-one amino acid) protein kinases mediate signaling from carbachol to p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and ternary complex factors. J Biol Chem 278:22278–22283 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

