Modulation of silent and constitutively active nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptors by potent receptor antagonists and Na+ ions in rat sympathetic neurons
- PMID: 20159949
- PMCID: PMC2872970
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.109.062208
Modulation of silent and constitutively active nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptors by potent receptor antagonists and Na+ ions in rat sympathetic neurons
Abstract
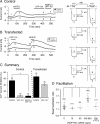
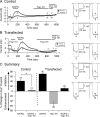
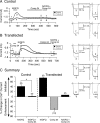
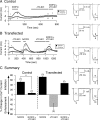
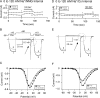
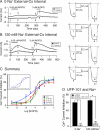
The pharmacology of G protein-coupled receptors can be influenced by factors such as constitutive receptor activation and Na(+) ions. In this study, we examined the coupling of natively and heterologously expressed nociceptin/orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) peptide (NOP) receptors with voltage-dependent Ca(2+) channels after exposure to four high-affinity NOP receptor blockers [[Nphe(1)Arg(14)Lys(15)]N/OFQ-NH(2) (UFP-101), 1-[1-(cyclooctylmethyl)-1,2,3,6-tetrahydro-5-(hydroxymethyl)-4-pyridinyl]-3-ethyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-benzimidazol-2-one (Trap-101), 1-benzyl-N-{3-[spiroisobenzofuran-1(3H),4'-piperidin-1-yl]propyl}pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide (compound 24), and N-(4-amino-2-methylquinolin-6-yl)-2-(4-ethylphenoxymethyl)benzamide hydrochloride (JTC-801)] in sympathetic neurons. The enhanced tonic inhibition of Ca(2+) currents in the absence of agonists, indicative of constitutively active NOP receptors in transfected neurons, was abolished after pretreatment with pertussis toxin. In control neurons, the four antagonists did not exert any effects when applied alone but significantly blocked the N/OFQ-mediated Ca(2+) current inhibition. Exposure of transfected neurons to UFP-101 resulted in partial agonist effects. In contrast, Trap-101, compound 24, and JTC-801 exerted inverse agonism, as measured by the loss of tonic Ca(2+) current inhibition. In experiments designed to measure the N/OFQ concentration-response relationship under varying Na(+) concentrations, a leftward shift of IC(50) values was observed after Na(+) exposure. Although similar N/OFQ efficacies were measured with all solutions, a significant decrease of Hill coefficient values was obtained with increasing Na(+) concentrations. Examination of the allosteric effects of Na(+) on heterologously overexpressed NOP receptors showed that the tonic Ca(2+) current inhibition was abolished in the presence of the monovalent cation. These results demonstrate that constitutively active NOP receptors exhibit differential blocker pharmacology and allosteric regulation by Na(+). Data are also presented demonstrating that heterologously expressed mu opioid receptors in sympathetic neurons are similarly modulated.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The biology of Nociceptin/Orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) related to obesity, stress, anxiety, mood, and drug dependence.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Mar;141(3):283-99. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.10.011. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24189487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
1-Benzyl-N-[3-[spiroisobenzofuran-1(3H),4'-piperidin-1-yl]propyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide (Compound 24) antagonizes NOP receptor-mediated potassium channel activation in rat periaqueductal gray slices.Eur J Pharmacol. 2009 Mar 15;606(1-3):84-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.01.036. Epub 2009 Feb 1. Eur J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19374842
-
[(pF)Phe4,Arg14,Lys15]N/OFQ-NH2 (UFP-102), a highly potent and selective agonist of the nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 Mar;312(3):1114-23. doi: 10.1124/jpet.104.077339. Epub 2004 Oct 27. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005. PMID: 15509719
-
Quantitative study of [(pF)Phe4,Arg14,Lys15]nociceptin/orphanin FQ-NH2 (UFP-102) at NOP receptors in rat periaqueductal gray slices.Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 Jan 28;579(1-3):110-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.10.006. Epub 2007 Oct 11. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 17976580
-
Nociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide receptors: pharmacology and clinical implications.Curr Drug Targets. 2007 Jan;8(1):117-35. doi: 10.2174/138945007779315605. Curr Drug Targets. 2007. PMID: 17266536 Review.
Cited by
-
NOP receptor pharmacological profile - A dynamic mass redistribution study.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 30;13(8):e0203021. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203021. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30161182 Free PMC article.
-
Role of nociceptin/orphanin FQ and NOP receptors in the response to acute and repeated restraint stress in rats.J Neuroendocrinol. 2012 Dec;24(12):1527-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2012.02361.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22835008 Free PMC article.
-
GRK2 Dictates a Functional Switch of the Peripheral Mu-Opioid Receptor.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020 Dec 16;11(24):4376-4386. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00622. Epub 2020 Nov 11. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33174729 Free PMC article.
-
Nociceptin receptor signaling in sympathetic neurons from septic rats.J Surg Res. 2013 Oct;184(2):973-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2013.03.076. Epub 2013 Apr 11. J Surg Res. 2013. PMID: 23608620 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Profile of Nociceptin/Orphanin FQ Receptors Interacting with G-Proteins and β-Arrestins 2.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 6;10(8):e0132865. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132865. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26248189 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andoh T, Itoh M, Kuraishi Y. (1997) Nociceptin gene expression in rat dorsal root ganglia induced by peripheral inflammation. Neuroreport 8:2793–2796 - PubMed
-
- Ardati A, Henningsen RA, Higelin J, Reinscheid RK, Civelli O, Monsma FJ., Jr (1997) Interaction of [3H]orphanin FQ and 125I-Tyr14-orphanin FQ with the orphanin FQ receptor: kinetics and modulation by cations and guanine nucleotides. Mol Pharmacol 51:816–824 - PubMed
-
- Barnes TA, McDonald J, Rowbotham DJ, Duarte TL, Lambert DG. (2007) Effects of receptor density on Nociceptin/OrphaninFQ peptide receptor desensitisation: studies using the ecdysone inducible expression system. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 376:217–225 - PubMed
-
- Beedle AM, McRory JE, Poirot O, Doering CJ, Altier C, Barrere C, Hamid J, Nargeot J, Bourinet E, Zamponi GW. (2004) Agonist-independent modulation of N-type calcium channels by ORL1 receptors. Nat Neurosci 7:118–125 - PubMed
-
- Briscini L, Corradini L, Ongini E, Bertorelli R. (2002) Up-regulation of ORL-1 receptors in spinal tissue of allodynic rats after sciatic nerve injury. Eur J Pharmacol 447:59–65 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

