Essential role of Tip60-dependent recruitment of ribonucleotide reductase at DNA damage sites in DNA repair during G1 phase
- PMID: 20159953
- PMCID: PMC2816732
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1863810
Essential role of Tip60-dependent recruitment of ribonucleotide reductase at DNA damage sites in DNA repair during G1 phase
Abstract
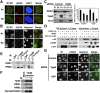
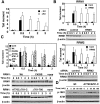
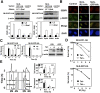
A balanced deoxyribonucleotide (dNTP) supply is essential for DNA repair. Here, we found that ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) subunits RRM1 and RRM2 accumulated very rapidly at damage sites. RRM1 bound physically to Tip60. Chromatin immunoprecipitation analyses of cells with an I-SceI cassette revealed that RRM1 bound to a damage site in a Tip60-dependent manner. Active RRM1 mutants lacking Tip60 binding failed to rescue an impaired DNA repair in RRM1-depleted G1-phase cells. Inhibition of RNR recruitment by an RRM1 C-terminal fragment sensitized cells to DNA damage. We propose that Tip60-dependent recruitment of RNR plays an essential role in dNTP supply for DNA repair.
Figures

References
-
- Dong Q, Wang TS. Mutational studies of human DNA polymerase α. Lysine 950 in the third most conserved region of α-like DNA polymerases is involved in binding the deoxynucleoside triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:21563–21570. - PubMed
-
- Fukushima M, Fujioka A, Uchida J, Nakagawa F, Takechi T. Thymidylate synthase (TS) and ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) may be involved in acquired resistance to 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) in human cancer xenografts in vivo. Eur J Cancer. 2001;37:1681–1687. - PubMed
-
- Guittet O, Hakansson P, Voevodskaya N, Fridd S, Graslund A, Arakawa H, Nakamura Y, Thelander L. Mammalian p53R2 protein forms an active ribonucleotide reductase in vitro with the R1 protein, which is expressed both in resting cells in response to DNA damage and in proliferating cells. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:40647–40651. - PubMed
-
- Hakansson P, Hofer A, Thelander L. Regulation of mammalian ribonucleotide reduction and dNTP pools after DNA damage and in resting cells. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:7834–7841. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
