The mammalian clock component PERIOD2 coordinates circadian output by interaction with nuclear receptors
- PMID: 20159955
- PMCID: PMC2816734
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.564110
The mammalian clock component PERIOD2 coordinates circadian output by interaction with nuclear receptors
Abstract
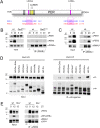
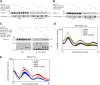
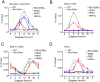
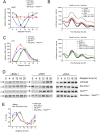
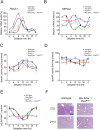
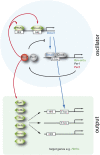
Mammalian circadian clocks provide a temporal framework to synchronize biological functions. To obtain robust rhythms with a periodicity of about a day, these clocks use molecular oscillators consisting of two interlocked feedback loops. The core loop generates rhythms by transcriptional repression via the Period (PER) and Cryptochrome (CRY) proteins, whereas the stabilizing loop establishes roughly antiphasic rhythms via nuclear receptors. Nuclear receptors also govern many pathways that affect metabolism and physiology. Here we show that the core loop component PER2 can coordinate circadian output with the circadian oscillator. PER2 interacts with nuclear receptors including PPARalpha and REV-ERBalpha and serves as a coregulator of nuclear receptor-mediated transcription. Consequently, PER2 is rhythmically bound at the promoters of nuclear receptor target genes in vivo. In this way, the circadian oscillator can modulate the expression of nuclear receptor target genes like Bmal1, Hnf1alpha, and Glucose-6-phosphatase. The concept that PER2 may propagate clock information to metabolic pathways via nuclear receptors adds an important facet to the clock-dependent regulation of biological networks.
Figures

Comment in
-
A wheel of time: the circadian clock, nuclear receptors, and physiology.Genes Dev. 2010 Apr 15;24(8):741-7. doi: 10.1101/gad.1920710. Genes Dev. 2010. PMID: 20395363 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albrecht U, Sun ZS, Eichele G, Lee CC. A differential response of two putative mammalian circadian regulators, mper1 and mper2, to light. Cell. 1997;91:1055–1064. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht U, Bordon A, Schmutz I, Ripperger J. The multiple facets of Per2. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2007;72:95–104. - PubMed
-
- Asher G, Gatfield D, Stratmann M, Reinke H, Dibner C, Kreppel F, Mostoslavsky R, Alt FW, Schibler U. SIRT1 regulates circadian clock gene expression through PER2 deacetylation. Cell. 2008;134:317–328. - PubMed
-
- Bae K, Jin X, Maywood ES, Hastings MH, Reppert SM, Weaver DR. Differential functions of mPer1, mPer2, and mPer3 in the SCN circadian clock. Neuron. 2001;30:525–536. - PubMed
-
- Balsalobre A, Brown SA, Marcacci L, Tronche F, Kellendonk C, Reichardt HM, Schutz G, Schibler U. Resetting of circadian time in peripheral tissues by glucocorticoid signaling. Science. 2000;289:2344–2347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
