Identification of a linear epitope in sortilin that partakes in pro-neurotrophin binding
- PMID: 20159974
- PMCID: PMC2852960
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.062364
Identification of a linear epitope in sortilin that partakes in pro-neurotrophin binding
Abstract
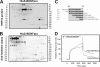
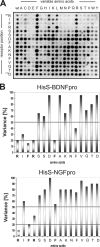
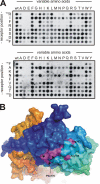
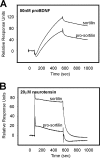
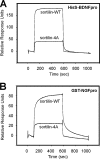
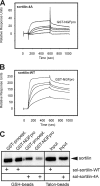
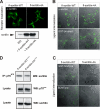
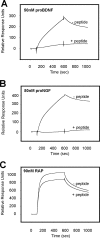
Sortilin acts as a cell surface receptor for pro-neurotrophins (pro-NT) that upon complex formation with the p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75(NTR)) is able to signal neuronal cell death. Here we screened a sortilin peptide library comprising 16-mer overlapping sequences for binding of the pro-domains of nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor. We find that a linear surface-exposed sequence, (163)RIFRSSDFAKNF(174), constitutes an important pro-NT binding epitope in sortilin. Systematic mutational analysis revealed residues Arg(163), Phe(165), Arg(166), and Phe(170) to be critical for the interaction. Expression of a sortilin mutant in which these four amino acids were substituted by alanines disrupted pro-NT binding without affecting receptor heterodimerization with p75(NTR) or binding of ligands that selectively engages the centrally located tunnel in the beta-propeller of sortilin. We furthermore demonstrate that a peptide comprising the ligand-binding epitope can prevent pro-NT-induced apoptosis in RN22 schwannoma cells.
Figures


References
-
- Willnow T. E., Petersen C. M., Nykjaer A. (2008) Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 9, 899–909 - PubMed
-
- Andersen O. M., Reiche J., Schmidt V., Gotthardt M., Spoelgen R., Behlke J., von Arnim C. A., Breiderhoff T., Jansen P., Wu X., Bales K. R., Cappai R., Masters C. L., Gliemann J., Mufson E. J., Hyman B. T., Paul S. M., Nykjaer A., Willnow T. E. (2005) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102, 13461–13466 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rogaeva E., Meng Y., Lee J. H., Gu Y., Kawarai T., Zou F., Katayama T., Baldwin C. T., Cheng R., Hasegawa H., Chen F., Shibata N., Lunetta K. L., Pardossi-Piquard R., Bohm C., Wakutani Y., Cupples L. A., Cuenco K. T., Green R. C., Pinessi L., Rainero I., Sorbi S., Bruni A., Duara R., Friedland R. P., Inzelberg R., Hampe W., Bujo H., Song Y. Q., Andersen O. M., Willnow T. E., Graff-Radford N., Petersen R. C., Dickson D., Der S. D., Fraser P. E., Schmitt-Ulms G., Younkin S., Mayeux R., Farrer L. A., St George-Hyslop P. (2007) Nat. Genet. 39, 168–177 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Scherzer C. R., Offe K., Gearing M., Rees H. D., Fang G., Heilman C. J., Schaller C., Levey A. I., Lah J. J. (2004) Arch. Neurol. 61, 1200–1205 - PubMed
-
- Clee S. M., Yandell B. S., Schueler K. M., Rabaglia M. E., Richards O. C., Raines S. M., Kabara E. A., Klass D. M., Mui E. T., Stapleton D. S., Gray-Keller M. P., Young M. B., Stoehr J. P., Lan H., Boronenkov I., Raess P. W., Flowers M. T., Attie A. D. (2006) Nat. Genet. 38, 688–693 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

