Hsp90 directly modulates the spatial distribution of AF9/MLLT3 and affects target gene expression
- PMID: 20159978
- PMCID: PMC2852934
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.101642
Hsp90 directly modulates the spatial distribution of AF9/MLLT3 and affects target gene expression
Abstract
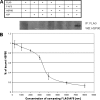
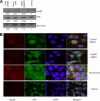
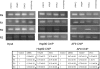
AF9/MLLT3 contributes to the regulation of the gene encoding the epithelial sodium channel alpha, ENaCalpha, in renal tubular cells. Specifically, increases in AF9 protein lead to a reduction in ENaCalpha expression and changes in AF9 activity appear to be an important component of aldosterone signaling in the kidney. Whereas AF9 is found in the nucleus where it interacts with the histone H3 lysine 79 methyltransferase, Dot1, AF9 is also present in the cytoplasm. Data presented in this report indicate that the heat shock protein Hsp90 directly and specifically interacts with AF9 as part of an Hsp90-Hsp70-p60/Hop chaperone complex. Experimental manipulation of Hsp90 function by the inhibitor novobiocin, but not 17-AAG, results in redistribution of AF9 from a primarily nuclear to cytoplasmic location. Knockdown of Hsp90 with siRNA mimics the effect elicited by novobiocin. As expected, a shift in AF9 from the nucleus to the cytoplasm in response to Hsp90 interference leads to increased ENaCalpha expression. This is accompanied by a decrease in AF9 occupancy at the ENaCalpha promoter. Our data suggest that the interaction of Hsp90, Hsp70, and p60/Hop with AF9 is necessary for the proper subnuclear localization and activity of AF9. AF9 is among a growing number of nuclear proteins recognized to rely on the Hsp90 complex for nuclear targeting.
Figures




References
-
- Krivtsov A. V., Twomey D., Feng Z., Stubbs M. C., Wang Y., Faber J., Levine J. E., Wang J., Hahn W. C., Gilliland D. G., Golub T. R., Armstrong S. A. (2006) Nature 442, 818–822 - PubMed
-
- DiMartino J. F., Miller T., Ayton P. M., Landewe T., Hess J. L., Cleary M. L., Shilatifard A. (2000) Blood 96, 3887–3893 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

