Three homologous subunits form a high affinity peptide-gated ion channel in Hydra
- PMID: 20159980
- PMCID: PMC2852933
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.059998
Three homologous subunits form a high affinity peptide-gated ion channel in Hydra
Abstract
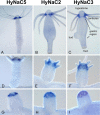
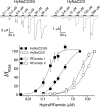
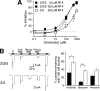
Recently, three ion channel subunits of the degenerin (DEG)/epithelial Na(+) channel (ENaC) gene family have been cloned from the freshwater polyp Hydra magnipapillata, the Hydra Na(+) channels (HyNaCs) 2-4. Two of them, HyNaC2 and HyNaC3, co-assemble to form an ion channel that is gated by the neuropeptides Hydra-RFamides I and II. The HyNaC2/3 channel is so far the only cloned ionotropic receptor from cnidarians and, together with the related ionotropic receptor FMRFamide-activated Na(+) channel (FaNaC) from snails, the only known peptide-gated ionotropic receptor. The HyNaC2/3 channel has pore properties, like a low Na(+) selectivity and a low amiloride affinity, that are different from other channels of the DEG/ENaC gene family, suggesting that a component of the native Hydra channel might still be lacking. Here, we report the cloning of a new ion channel subunit from Hydra, HyNaC5. The new subunit is closely related to HyNaC2 and -3 and co-localizes with HyNaC2 and -3 to the base of the tentacles. Coexpression in Xenopus oocytes of HyNaC5 with HyNaC2 and -3 largely increases current amplitude after peptide stimulation and affinity of the channel to Hydra-RFamides I and II. Moreover, the HyNaC2/3/5 channel has altered pore properties and amiloride affinity, more similarly to other DEG/ENaC channels. Collectively, our results suggest that the three homologous subunits HyNaC2, -3, and -5 form a peptide-gated ion channel in Hydra that could contribute to fast synaptic transmission.
Figures





References
-
- Kellenberger S., Schild L. (2002) Physiol. Rev. 82, 735–767 - PubMed
-
- Ainsley J. A., Pettus J. M., Bosenko D., Gerstein C. E., Zinkevich N., Anderson M. G., Adams C. M., Welsh M. J., Johnson W. A. (2003) Curr. Biol. 13, 1557–1563 - PubMed
-
- Liu L., Leonard A. S., Motto D. G., Feller M. A., Price M. P., Johnson W. A., Welsh M. J. (2003) Neuron 39, 133–146 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

