Methylation of ribosomal protein S10 by protein-arginine methyltransferase 5 regulates ribosome biogenesis
- PMID: 20159986
- PMCID: PMC2857073
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.103911
Methylation of ribosomal protein S10 by protein-arginine methyltransferase 5 regulates ribosome biogenesis
Abstract
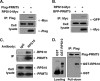
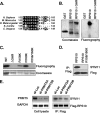
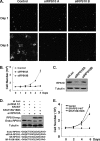
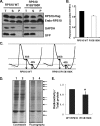
Modulation of ribosomal assembly is a fine tuning mechanism for cell number and organ size control. Many ribosomal proteins undergo post-translational modification, but their exact roles remain elusive. Here, we report that ribosomal protein s10 (RPS10) is a novel substrate of an oncoprotein, protein-arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5). We show that PRMT5 interacts with RPS10 and catalyzes its methylation at the Arg(158) and Arg(160) residues. The methylation of RPS10 at Arg(158) and Arg(160) plays a role in the proper assembly of ribosomes, protein synthesis, and optimal cell proliferation. The RPS10-R158K/R160K mutant is not efficiently assembled into ribosomes and is unstable and prone to degradation by the proteasomal pathway. In nucleoli, RPS10 interacts with nucleophosmin/B23 and is predominantly concentrated in the granular component region, which is required for ribosome assembly. The RPS10 methylation mutant interacts weakly with nucleophosmin/B23 and fails to concentrate in the granular component region. Our results suggest that PRMT5 is likely to regulate cell proliferation through the methylation of ribosome proteins, and thus reveal a novel mechanism for PRMT5 in tumorigenesis.
Figures
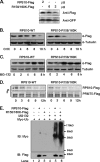
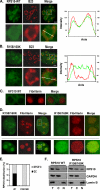
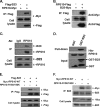
References
-
- Ruggero D., Pandolfi P. P. (2003) Nat. Rev. Cancer 3, 179–192 - PubMed
-
- Polevoda B., Sherman F. (2007) Mol. Microbiol. 65, 590–606 - PubMed
-
- Scolnik P. A., Eliceiri G. L. (1979) Eur. J. Biochem. 101, 93–101 - PubMed
-
- Lhoest J., Lobet Y., Costers E., Colson C. (1984) Eur. J. Biochem. 141, 585–590 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

