Leptospiral endostatin-like protein A is a bacterial cell surface receptor for human plasminogen
- PMID: 20160016
- PMCID: PMC2863546
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01282-09
Leptospiral endostatin-like protein A is a bacterial cell surface receptor for human plasminogen
Abstract
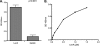
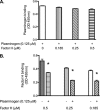
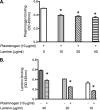
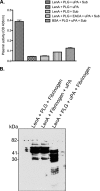
The spirochete Leptospira interrogans is a highly invasive pathogen of worldwide public health importance. Studies from our laboratories and another have demonstrated that L. interrogans can acquire host plasminogen on its surface. Exogenous plasminogen activators can then convert bound plasminogen into the functionally active protease plasmin. In this study, we extend upon those observations and report that leptospiral endostatin-like protein A (LenA) binds human plasminogen in a dose-dependent manner. LenA-plasminogen interactions were significantly inhibited by the lysine analog xi-aminocaproic acid, suggesting that the lysine-binding sites on the amino-terminal kringle portion of the plasminogen molecule play a role in the binding. Previous studies have shown that LenA also binds complement regulator factor H and the extracellular matrix component laminin. Plasminogen competed with both factor H and laminin for binding to LenA, which suggests overlapping ligand-binding sites on the bacterial receptor. Finally, LenA-bound plasminogen could be converted to plasmin, which in turn degraded fibrinogen, suggesting that acquisition of host-derived plasmin by LenA may aid bacterial dissemination throughout host tissues.
Figures

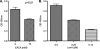
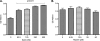
Similar articles
-
The novel leptospiral surface adhesin Lsa20 binds laminin and human plasminogen and is probably expressed during infection.Infect Immun. 2011 Nov;79(11):4657-67. doi: 10.1128/IAI.05583-11. Epub 2011 Aug 15. Infect Immun. 2011. PMID: 21844229 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmin cleaves fibrinogen and the human complement proteins C3b and C5 in the presence of Leptospira interrogans proteins: A new role of LigA and LigB in invasion and complement immune evasion.Immunobiology. 2016 May;221(5):679-89. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2016.01.001. Epub 2016 Jan 7. Immunobiology. 2016. PMID: 26822552
-
Features of two proteins of Leptospira interrogans with potential role in host-pathogen interactions.BMC Microbiol. 2012 Mar 30;12:50. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-12-50. BMC Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22463075 Free PMC article.
-
A Review on Host-Leptospira Interactions: What We Know and Future Expectations.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Nov 25;11:777709. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.777709. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34900757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leptospiral extracellular matrix adhesins as mediators of pathogen-host interactions.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2014 Mar;352(2):129-39. doi: 10.1111/1574-6968.12349. Epub 2013 Dec 11. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2014. PMID: 24289724 Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro identification of novel plasminogen-binding receptors of the pathogen Leptospira interrogans.PLoS One. 2010 Jun 22;5(6):e11259. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011259. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20582320 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus manganese transport protein C (MntC) is an extracellular matrix- and plasminogen-binding protein.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 19;9(11):e112730. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112730. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25409527 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium binding to leptospira outer membrane antigen LipL32 is not necessary for its interaction with plasma fibronectin, collagen type IV, and plasminogen.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 10;287(7):4826-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.277210. Epub 2011 Dec 6. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22147698 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of novel OmpA-like protein of Leptospira interrogans that binds extracellular matrix molecules and plasminogen.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e21962. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021962. Epub 2011 Jul 6. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21755014 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of three novel adhesins of Leptospira interrogans.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2013 Dec;89(6):1103-16. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.13-0205. Epub 2013 Aug 19. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2013. PMID: 23958908 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benedek, O., J. Bene, B. Melegh, and L. Emody. 2003. Mapping of possible laminin binding sites of Y. pestis plasminogen activator (Pla) via phage display. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 529:101-104. - PubMed
-
- Benedek, O., A. S. Khan, G. Schneider, G. Nagy, R. Autar, R. J. Pieters, and L. Emody. 2005. Identification of laminin-binding motifs of Yersinia pestis plasminogen activator by phage display. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 295:87-98. - PubMed
-
- Berge, A., and U. Sjobring. 1993. PAM, a novel plasminogen-binding protein from Streptococcus pyogenes. J. Biol. Chem. 268:25417-25424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

