Celastrol suppresses angiogenesis-mediated tumor growth through inhibition of AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway
- PMID: 20160026
- PMCID: PMC2854134
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3201
Celastrol suppresses angiogenesis-mediated tumor growth through inhibition of AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway
Erratum in
-
Correction: Celastrol Suppresses Angiogenesis-Mediated Tumor Growth through Inhibition of AKT/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Pathway.Cancer Res. 2019 Feb 1;79(3):685. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-3859. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30709873 No abstract available.
Abstract
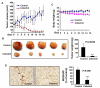
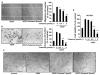
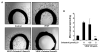
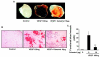
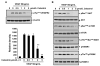
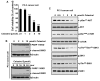
Understanding the molecular basis and target of traditional medicine is critical for drug development. Celastrol, derived from Trypterygium wilfordii Hook F. ("Thunder of God Vine"), a traditional Chinese medicine plant, has been assigned anticancer activities, but its mechanism is not well understood. Here, we investigated whether Celastrol could inhibit angiogenesis-mediated tumor growth and, if so, through what mechanism. When given s.c. to mice bearing human prostate cancer (PC-3 cell) xenografts, Celastrol (2 mg/kg/d) significantly reduced the volume and the weight of solid tumors and decreased tumor angiogenesis. We found that this agent inhibited vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced proliferation, migration, invasion, and capillary-like structure formation by primary cultured human umbilical vascular endothelial cells (HUVEC) in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, Celastrol abrogated VEGF-induced sprouting of the vessels from aortic rings and inhibited vascular formation in the Matrigel plug assay in vivo. To understand the molecular mechanism of these activities, we next examined the signaling pathways in treated HUVECs and PC-3 tumor cells. Celastrol suppressed the VEGF-induced activation of AKT, mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), and ribosomal protein S6 kinase (P70S6K). Additionally, we found that Celastrol inhibited the proliferation of prostate cancer cells and induced apoptosis, and these effects correlated with the extent of inhibition of AKT/mTOR/P70S6K signaling. Taken together, our results suggest that Celastrol targets the AKT/mTOR/P70S6K pathway, which leads to suppression of tumor growth and angiogenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ginsenoside Rd regulates the Akt/mTOR/p70S6K signaling cascade and suppresses angiogenesis and breast tumor growth.Oncol Rep. 2017 Jul;38(1):359-367. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5652. Epub 2017 May 19. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28534996
-
Quercetin inhibits angiogenesis mediated human prostate tumor growth by targeting VEGFR- 2 regulated AKT/mTOR/P70S6K signaling pathways.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47516. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047516. Epub 2012 Oct 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23094058 Free PMC article.
-
SB365 inhibits angiogenesis and induces apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma through modulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.Cancer Sci. 2012 Nov;103(11):1929-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2012.02409.x. Epub 2012 Sep 25. Cancer Sci. 2012. PMID: 22909393 Free PMC article.
-
Celastrol as an emerging anticancer agent: Current status, challenges and therapeutic strategies.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Jul;163:114882. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114882. Epub 2023 May 15. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37196541 Review.
-
Targeting vasculature in urologic tumors: mechanistic and therapeutic significance.J Cell Biochem. 2008 Feb 15;103(3):691-708. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21442. J Cell Biochem. 2008. PMID: 17668426 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Luteolin inhibits human prostate tumor growth by suppressing vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2-mediated angiogenesis.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52279. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052279. Epub 2012 Dec 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23300633 Free PMC article.
-
Cinobufagin suppresses colorectal cancer angiogenesis by disrupting the endothelial mammalian target of rapamycin/hypoxia-inducible factor 1α axis.Cancer Sci. 2019 May;110(5):1724-1734. doi: 10.1111/cas.13988. Epub 2019 Mar 29. Cancer Sci. 2019. PMID: 30839155 Free PMC article.
-
YLT192, a novel, orally active bioavailable inhibitor of VEGFR2 signaling with potent antiangiogenic activity and antitumor efficacy in preclinical models.Sci Rep. 2014 Aug 12;4:6031. doi: 10.1038/srep06031. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 25112436 Free PMC article.
-
Celastrol, an active constituent of the TCM plant Tripterygium wilfordii Hook.f., inhibits prostate cancer bone metastasis.Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2017 Jun;20(2):156-164. doi: 10.1038/pcan.2016.61. Epub 2017 Feb 14. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2017. PMID: 28195223
-
HDAC10 promotes angiogenesis in endothelial cells through the PTPN22/ERK axis.Oncotarget. 2017 May 24;8(37):61338-61349. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18130. eCollection 2017 Sep 22. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28977867 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tao X, Cush JJ, Garret M, Lipsky PE. A phase I study of ethyl acetate extract of the chinese antirheumatic herb Tripterygium wilfordii hook F in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2001;28:2160–7. - PubMed
-
- Li H, Zhang YY, Tan HW, Jia YF, Li D. Therapeutic effect of tripterine on adjuvant arthritis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008;118:479–84. - PubMed
-
- Li H, Zhang YY, Huang XY, Sun YN, Jia YF, Li D. Beneficial effect of tripterine on systemic lupus erythematosus induced by active chromatin in BALB/c mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005;512:231–7. - PubMed
-
- Kiaei M, Kipiani K, Petri S, Chen J, Calingasan NY, Beal MF. Celastrol blocks neuronal cell death and extends life in transgenic mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurodegener Dis. 2005;2:246–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

