Protein kinase D1 inhibits cell proliferation through matrix metalloproteinase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 secretion in prostate cancer
- PMID: 20160036
- PMCID: PMC3197700
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4155
Protein kinase D1 inhibits cell proliferation through matrix metalloproteinase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 secretion in prostate cancer
Abstract
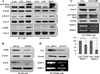
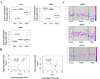
We and others previously showed that protein kinase D1 (PKD1) is downregulated in several cancers including prostate; interacts with E-cadherin, a major cell adhesion epithelial protein; and causes increased cell aggregation and decreased motility of prostate cancer cells. In this study, we show that PKD1 complexes with beta3-integrin, resulting in activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) kinase-ERK pathway, which causes increased production of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9, that is associated with shedding of soluble 80 kDa E-cadherin extracellular domain. Interestingly, decreased cell proliferation following PKD1 transfection was rescued by MMP-2 and MMP-9 inhibitors and augmented by recombinant MMP-2 (rMMP-2) and rMMP-9 proteins, suggesting an antiproliferative role for MMPs in prostate cancer. Translational studies by in silico analysis of publicly available DNA microarray data sets show a significant direct correlation between PKD1 and MMP-2 expression in human prostate tissues. The study shows a novel mechanism for antiproliferative effects of PKD1, a protein of emerging translational interest in several human cancers, through increased production of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in cancer cells.
Figures




References
-
- Frisch SM, Ruoslahti E. Integrins and anoikis. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997;9:701–706. - PubMed
-
- Kantak SS, Kramer RH. E-cadherin regulates anchorage-independent growth and survival in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:16953–16961. - PubMed
-
- Stetler-Stevenson WG, Krutzsch HC, Wacher MP, Margulies IM, Liotta LA. The activation of human type IV collagenase proenzyme. Sequence identification of the major conversion product following organomercurial activation. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:1353–1356. - PubMed
-
- McCawley LJ, Matrisian LM. Matrix metalloproteinases: they're not just for matrix anymore! Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001;13:534–540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

