Neural differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells follows developmental principles but with variable potency
- PMID: 20160098
- PMCID: PMC2840097
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0910012107
Neural differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells follows developmental principles but with variable potency
Abstract
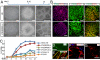
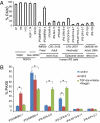
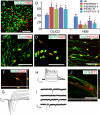
For the promise of human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) to be realized, it is necessary to ask if and how efficiently they may be differentiated to functional cells of various lineages. Here, we have directly compared the neural-differentiation capacity of human iPSCs and embryonic stem cells (ESCs). We have shown that human iPSCs use the same transcriptional network to generate neuroepithelia and functionally appropriate neuronal types over the same developmental time course as hESCs in response to the same set of morphogens; however, they do it with significantly reduced efficiency and increased variability. These results were consistent across iPSC lines and independent of the set of reprogramming transgenes used to derive iPSCs as well as the presence or absence of reprogramming transgenes in iPSCs. These findings, which show a need for improving differentiation potency of iPSCs, suggest the possibility of employing human iPSCs in pathological studies, therapeutic screening, and autologous cell transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: J.A.T. is a founder, stock owner, consultant, and board member of Cellular Dynamics International (CDI). He also serves as a scientific advisor to and has financial interests in Tactics II Stem Cell Ventures.
Figures

References
-
- Li XJ, et al. Specification of motoneurons from human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23:215–221. - PubMed
-
- Roy NS, et al. Functional engraftment of human ES cell-derived dopaminergic neurons enriched by coculture with telomerase-immortalized midbrain astrocytes. Nat Med. 2006;12:1259–1268. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe K, et al. A ROCK inhibitor permits survival of dissociated human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:681–686. - PubMed
-
- Yang L, et al. Human cardiovascular progenitor cells develop from a KDR+ embryonic-stem-cell-derived population. Nature. 2008;453:524–528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

