Inhibin-A antagonizes TGFbeta2 signaling by down-regulating cell surface expression of the TGFbeta coreceptor betaglycan
- PMID: 20160125
- PMCID: PMC2840806
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2008-0374
Inhibin-A antagonizes TGFbeta2 signaling by down-regulating cell surface expression of the TGFbeta coreceptor betaglycan
Abstract
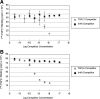
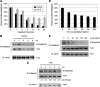
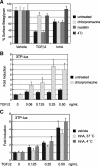
Inhibin is an atypical member of the TGFbeta family of signaling ligands and is classically understood to function via competitive antagonism of activin ligand binding. Inhibin-null (Inha-/-) mice develop both gonadal and adrenocortical tumors, the latter of which depend upon gonadectomy for initiation. We have previously shown that gonadectomy initiates adrenal tumorigenesis in Inha-/- mice by elevating production of LH, which drives aberrant proliferation and differentiation of subcapsular adrenocortical progenitor cells. In this study, we demonstrate that LH signaling specifically up-regulates expression of TGFbeta2 in the subcapsular region of the adrenal cortex, which coincides with regions of aberrant Smad3 activation in Inha-/- adrenal glands. Consistent with a functional interaction between inhibin and TGFbeta2, we further demonstrate that recombinant inhibin-A antagonizes signaling by TGFbeta2 in cultured adrenocortical cells. The mechanism of this antagonism depends upon the mutual affinity of inhibin-A and TGFbeta2 for the signaling coreceptor betaglycan. Although inhibin-A cannot physically displace TGFbeta2 from its binding sites on betaglycan, binding of inhibin-A to the cell surface causes endocytic internalization of betaglycan, thereby reducing the number of available binding sites for TGFbeta2 on the cell surface. The mechanism by which inhibin-A induces betaglycan internalization is clathrin independent, making it distinct from the mechanism by which TGFbeta ligands themselves induce betaglycan internalization. These data indicate that inhibin can specifically antagonize TGFbeta2 signaling in cellular contexts where surface expression of betaglycan is limiting and provide a novel mechanism for activin-independent phenotypes in Inha-/- mice.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transforming growth factor-beta modulates inhibin A bioactivity in the LbetaT2 gonadotrope cell line by competing for binding to betaglycan.Mol Endocrinol. 2002 Dec;16(12):2754-63. doi: 10.1210/me.2002-0014. Mol Endocrinol. 2002. PMID: 12456797
-
Transforming growth factor-beta blocks inhibin binding to different target cell types in a context-dependent manner through dual mechanisms involving betaglycan.Endocrinology. 2007 Nov;148(11):5355-68. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-0155. Epub 2007 Jul 26. Endocrinology. 2007. PMID: 17656464
-
Expression of activin and inhibin subunits, receptors and binding proteins in human adrenocortical neoplasms.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2006 Dec;65(6):792-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2006.02668.x. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2006. PMID: 17121532
-
A Tale of Two Proteins: Betaglycan, IGSF1, and the Continuing Search for the Inhibin B Receptor.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Jan;31(1):37-45. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2019.08.014. Epub 2019 Oct 22. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 31648935 Review.
-
Molecular biology of inhibin action.Semin Reprod Med. 2004 Aug;22(3):269-76. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-831902. Semin Reprod Med. 2004. PMID: 15319829 Review.
Cited by
-
The molecular mechanism of ovarian granulosa cell tumors.J Ovarian Res. 2018 Feb 6;11(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13048-018-0384-1. J Ovarian Res. 2018. PMID: 29409506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adrenocortical stem and progenitor cells: unifying model of two proposed origins.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011 Apr 10;336(1-2):206-12. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2010.11.012. Epub 2010 Nov 20. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21094677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional regulation by normal epithelium of premalignant to malignant progression in Barrett's esophagus.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 12;6:35227. doi: 10.1038/srep35227. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27731371 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Soluble TGF-β Receptors in Addition to Soluble Endoglin Are Elevated in Preeclamptic Serum and They Synergistically Inhibit TGF-β Signaling.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Aug 1;102(8):3065-3074. doi: 10.1210/jc.2017-01150. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28633389 Free PMC article.
-
Organ Boundary Circuits Regulate Sox9+ Alveolar Tuft Cells During Post-Pneumonectomy Lung Regeneration.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 8:2024.01.07.574469. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.07.574469. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38260691 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Chang H, Brown CW, Matzuk MM 2002 Genetic analysis of the mammalian transforming growth factor-β superfamily. Endocr Rev 23:787–823 - PubMed
-
- Matzuk MM, Lamb DJ 2002 Genetic dissection of mammalian fertility pathways. Nat Cell Biol 4(Suppl):s41–s49 - PubMed
-
- Cook RW, Thompson TB, Jardetzky TS, Woodruff TK 2004 Molecular biology of inhibin action. Semin Reprod Med 22:269–276 - PubMed
-
- Ethier JF, Findlay JK 2001 Roles of activin and its signal transduction mechanisms in reproductive tissues. Reproduction 121:667–675 - PubMed
-
- Massagué J, Seoane J, Wotton D 2005 Smad transcription factors. Genes Dev 19:2783–2810 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

