Inhibin-A antagonizes TGFbeta2 signaling by down-regulating cell surface expression of the TGFbeta coreceptor betaglycan
- PMID: 20160125
- PMCID: PMC2840806
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2008-0374
Inhibin-A antagonizes TGFbeta2 signaling by down-regulating cell surface expression of the TGFbeta coreceptor betaglycan
Abstract
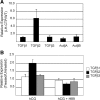
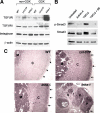
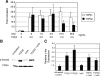
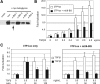
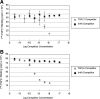
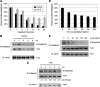
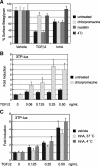
Inhibin is an atypical member of the TGFbeta family of signaling ligands and is classically understood to function via competitive antagonism of activin ligand binding. Inhibin-null (Inha-/-) mice develop both gonadal and adrenocortical tumors, the latter of which depend upon gonadectomy for initiation. We have previously shown that gonadectomy initiates adrenal tumorigenesis in Inha-/- mice by elevating production of LH, which drives aberrant proliferation and differentiation of subcapsular adrenocortical progenitor cells. In this study, we demonstrate that LH signaling specifically up-regulates expression of TGFbeta2 in the subcapsular region of the adrenal cortex, which coincides with regions of aberrant Smad3 activation in Inha-/- adrenal glands. Consistent with a functional interaction between inhibin and TGFbeta2, we further demonstrate that recombinant inhibin-A antagonizes signaling by TGFbeta2 in cultured adrenocortical cells. The mechanism of this antagonism depends upon the mutual affinity of inhibin-A and TGFbeta2 for the signaling coreceptor betaglycan. Although inhibin-A cannot physically displace TGFbeta2 from its binding sites on betaglycan, binding of inhibin-A to the cell surface causes endocytic internalization of betaglycan, thereby reducing the number of available binding sites for TGFbeta2 on the cell surface. The mechanism by which inhibin-A induces betaglycan internalization is clathrin independent, making it distinct from the mechanism by which TGFbeta ligands themselves induce betaglycan internalization. These data indicate that inhibin can specifically antagonize TGFbeta2 signaling in cellular contexts where surface expression of betaglycan is limiting and provide a novel mechanism for activin-independent phenotypes in Inha-/- mice.
Figures
References
-
- Chang H, Brown CW, Matzuk MM 2002 Genetic analysis of the mammalian transforming growth factor-β superfamily. Endocr Rev 23:787–823 - PubMed
-
- Matzuk MM, Lamb DJ 2002 Genetic dissection of mammalian fertility pathways. Nat Cell Biol 4(Suppl):s41–s49 - PubMed
-
- Cook RW, Thompson TB, Jardetzky TS, Woodruff TK 2004 Molecular biology of inhibin action. Semin Reprod Med 22:269–276 - PubMed
-
- Ethier JF, Findlay JK 2001 Roles of activin and its signal transduction mechanisms in reproductive tissues. Reproduction 121:667–675 - PubMed
-
- Massagué J, Seoane J, Wotton D 2005 Smad transcription factors. Genes Dev 19:2783–2810 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

