Investigation of variants identified in caucasian genome-wide association studies for plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglycerides levels in Mexican dyslipidemic study samples
- PMID: 20160193
- PMCID: PMC2827864
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.109.908004
Investigation of variants identified in caucasian genome-wide association studies for plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglycerides levels in Mexican dyslipidemic study samples
Abstract
Background: Although epidemiological studies have demonstrated an increased predisposition to low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and high triglyceride levels in the Mexican population, Mexicans have not been included in any of the previously reported genome-wide association studies for lipids.
Methods and results: We investigated 6 single-nucleotide polymorphisms associated with triglycerides, 7 with high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and 1 with both triglycerides and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in recent Caucasian genome-wide association studies in Mexican familial combined hyperlipidemia families and hypertriglyceridemia case-control study samples. These variants were within or near the genes ABCA1, ANGPTL3, APOA5, APOB, CETP, GALNT2, GCKR, LCAT, LIPC, LPL (2), MMAB-MVK, TRIB1, and XKR6-AMAC1L2. We performed a combined analysis of the family-based and case-control studies (n=2298) using the Z method to combine statistics. Ten of the single-nucleotide polymorphisms were nominally significant and 5 were significant after Bonferroni correction (P=2.20 x 10(-3) to 2.6 x 10(-11)) for the number of tests performed (APOA5, CETP, GCKR, and GALNT2). Interestingly, our strongest signal was obtained for triglycerides with the minor allele of rs964184 (P=2.6 x 10(-11)) in the APOA1/C3/A4/A5 gene cluster region that is significantly more common in Mexicans (27%) than in whites (12%).
Conclusions: It is important to confirm whether known loci have a consistent effect across ethnic groups. We show replication of 5 Caucasian genome-wide association studies lipid associations in Mexicans. The remaining loci will require a comprehensive investigation to exclude or verify their significance in Mexicans. We also demonstrate that rs964184 has a large effect (odds ratio, 1.74) and is more frequent in the Mexican population, and thus it may contribute to the high predisposition to dyslipidemias in Mexicans.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
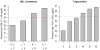
References
-
- Lloyd-Jones D, Adams R, Carnethon M, De Simone G, Ferguson T, Flegal K, Ford E, Furie K, Go A, Greenlund K, Haase N, Hailpern S, Ho M, Howard V, Kissela B, Kittner S, Lackland D, Lisabeth L, Marelli A, McDermott M, Meigs J, Mozaffarian D, Nichol G, O'Donnell C, Roger V, Rosamond W, Sacco R, Sorlie P, Stafford R, Steinberger J, Thom T, Wasserthiel-Smoller S, Wong N, Wylie-Rosett J, Hong Y. Heart disease and stroke statistics -- 2009 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2009;119:480–6. - PubMed
-
- Aguilar-Salinas C, Olaiz G, Valles V, Torres J, Gomez Perez F, Rull J, Rojas R, Franco A, Sepulveda J. High prevalence of low HDL cholesterol concentrations and mixed hyperlipidemia in a Mexican nationwide survey. J Lipid Res. 2001;42:1298–307. - PubMed
-
- Aguilar-Salinas CA, Rojas R, Gómez-Pérez FJ, Valles V, Ríos-Torres JM, Franco A, Olaiz G, Rull JA, Sepúlveda J. High prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Mexico. Archives of Medical Research. 2004;35:76–81. - PubMed
-
- Kathiresan S, Willer C, Peloso G, Demissie S, Musunuru K, Schadt E, Kaplan L, Bennett D, Li Y, Tanaka T, Voight B, Bonnycastle L, Jackson A, Crawford G, Surti A, Guiducci C, Burtt N, Parish S, Clarke R, Zelenika D, Kubalanza K, Morken M, Scott L, Stringham H, Galan P, Swift A, Kuusisto J, Bergman R, Sundvall J, Laakso M, Ferrucci L, Scheet P, Sanna S, Uda M, Yang Q, Lunetta K, Dupuis J, de Bakker P, O'Donnell C, Chambers J, Kooner J, Hercberg S, Meneton P, Lakatta E, Scuteri A, Schlessinger D, Tuomilehto J, Collins F, Groop L, Altshuler D, Collins R, Lathrop G, Melander O, Salomaa V, Peltonen L, Orho-Melander M, Ordovas J, Boehnke M, Abecasis G, Mohlke K, Cupples L. Common variants at 30 loci contribute to polygenic dyslipidemia. Nat Genet. 2009;41:56–65. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

