A simple algorithm to assess patient suitability for Calypso-seed implantation for four-dimensional prostate localization
- PMID: 20160683
- PMCID: PMC5719784
- DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v11i1.3107
A simple algorithm to assess patient suitability for Calypso-seed implantation for four-dimensional prostate localization
Abstract
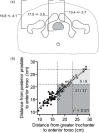
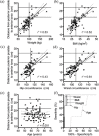
To retrospectively determine the proportion of prostate cancer patients who are appropriate candidates for prostate localization with Calypso (Calypso Medical, Seattle, WA); to assess the accuracy of surface anatomy in predicting prostate depth; and to describe a simple clinical algorithm predicting patient's appropriateness for Calypso localization. Medical records and archived CT scans of all patients treated for localized prostate cancer at our institution between 2006 and 2007 were reviewed. Association between the feasibility of Calypso use, the depth of the prostate from the anterior torso, and a variety of anatomic factors were assessed (ANOVA, linear regression, and ROC). Patients were appropriate for the Calypso system in 91% of cases (localize and track, 52%; localize only, 39%). Strong correlation between greater trochanter location and the posterior prostate was seen (r 2 = 0.91, mean difference 0.6 cm). The negative predictive value of the greater trochanter measurements was 31%. Thirty-one out of forty-five patients (69%) who were deemed inappropriate for Calypso based on greater trochanter to anterior torso measurements were eligible on the basis of CT-based measurements of prostate depth. Weight, BMI, waist circumference, and hip circumference correlated with distance from the prostate to the anterior torso and were predictive of Calypso appropriateness. All patients with weight <or= 100 kg, BMI <or= 30, or waist/hip circumference <or= 100 cm, were eligible for Calypso. Most prostate cancer patients are candidates for Calypso localization +/- tracking. The greater trochanter to anterior torso distance underestimates the number of eligible patients. Weight, BMI and waist/hip circumference are good predictors for Calypso appropriateness.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the preimplantation worksheet in determining Calypso eligibility for men prescribed postprostatectomy radiotherapy with electromagnetic transponder guidance.Med Dosim. 2017 Autumn;42(3):223-229. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2017.05.003. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Med Dosim. 2017. PMID: 28648818
-
Electromagnetic Transponder Localization and Real-Time Tracking for Prostate Cancer Radiation Therapy: Clinical Impact of Metallic Hip Prostheses.Pract Radiat Oncol. 2020 Nov-Dec;10(6):e538-e542. doi: 10.1016/j.prro.2020.03.003. Epub 2020 Mar 19. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32201320
-
Comparison of transabdominal ultrasound and electromagnetic transponders for prostate localization.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2010 Jan 6;11(1):2924. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v11i1.2924. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2010. PMID: 20160686 Free PMC article.
-
[Prostate localization systems for prostate radiotherapy].Cancer Radiother. 2006 Nov;10(6-7):394-401. doi: 10.1016/j.canrad.2006.09.002. Epub 2006 Oct 10. Cancer Radiother. 2006. PMID: 17035061 Review. French.
-
Body size and composition and prostate cancer risk: systematic review and meta-regression analysis.Cancer Causes Control. 2006 Oct;17(8):989-1003. doi: 10.1007/s10552-006-0049-z. Cancer Causes Control. 2006. PMID: 16933050
References
-
- Willoughby TR, Kupelian PA, Pouliot J, et al. Target localization and real‐time tracking using the Calypso 4D localization system in patients with localized prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;65(2):528–34. - PubMed
-
- Kupelian P, Willoughby T, Mahadevan A, et al. Multi‐institutional clinical experience with the Calypso System in localization and continuous, real‐time monitoring of the prostate gland during external radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;67(4):1088–98. - PubMed
-
- Balter JM, Wright JN, Newell LJ, et al. Accuracy of a wireless localization system for radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;61(3):933–37. - PubMed
-
- Seiler PG, Blattmann H, Kirsch S, Muench RK, Ch S. A novel tracking technique for the continuous precise measurement of tumour positions in conformal radiotherapy. Physi Med Biol. 2000;45(9):N103–10. - PubMed
-
- Langen KM, Willoughby TR, Meeks SL, et al. Observations on real‐time prostate gland motion using electromagnetic tracking. Intl J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;71(4):1084–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

