Comparison of transabdominal ultrasound and electromagnetic transponders for prostate localization
- PMID: 20160686
- PMCID: PMC5719783
- DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v11i1.2924
Comparison of transabdominal ultrasound and electromagnetic transponders for prostate localization
Abstract
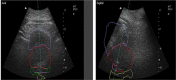
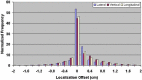
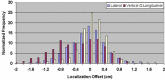
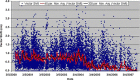
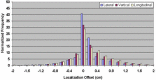
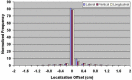
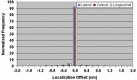
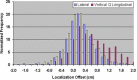
The aim of this study is to compare two methodologies of prostate localization in a large cohort of patients. Daily prostate localization using B-mode ultrasound has been performed at the Nebraska Medical Center since 2000. More recently, a technology using electromagnetic transponders implanted within the prostate was introduced into our clinic (Calypso(R)). With each technology, patients were localized initially using skin marks. Localization error distributions were determined from offsets between the initial setup positions and those determined by ultrasound or Calypso. Ultrasound localization data was summarized from 16619 imaging sessions spanning 7 years; Calypso localization data consists of 1524 fractions in 41 prostate patients treated in the course of a clinical trial at five institutions and 640 localizations from the first 16 patients treated with our clinical system. Ultrasound and Calypso patients treated between March and September 2007 at the Nebraska Medical Center were analyzed and compared, allowing a single institutional comparison of the two technologies. In this group of patients, the isocenter determined by ultrasound-based localization is on average 5.3 mm posterior to that determined by Calypso, while the systematic and random errors and PTV margins calculated from the ultrasound localizations were 3 - 4 times smaller than those calculated from the Calypso localizations. Our study finds that there are systematic differences between Calypso and ultrasound for prostate localization.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A comparison of radiographic techniques and electromagnetic transponders for localization of the prostate.Radiat Oncol. 2012 Jun 21;7:101. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-7-101. Radiat Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22720845 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of multiple image-based modalities for image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) of prostate carcinoma: a prospective study.Med Phys. 2013 Apr;40(4):041707. doi: 10.1118/1.4794502. Med Phys. 2013. PMID: 23556877 Clinical Trial.
-
Multi-institutional clinical experience with the Calypso System in localization and continuous, real-time monitoring of the prostate gland during external radiotherapy.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007 Mar 15;67(4):1088-98. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.10.026. Epub 2006 Dec 21. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007. PMID: 17187940
-
Target localization and real-time tracking using the Calypso 4D localization system in patients with localized prostate cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006 Jun 1;65(2):528-34. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.01.050. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006. PMID: 16690435
-
Prostate tumor alignment and continuous, real-time adaptive radiation therapy using electromagnetic fiducials: clinical and cost-utility analyses.Urol Oncol. 2009 Sep-Oct;27(5):473-82. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2008.04.017. Epub 2008 Jul 14. Urol Oncol. 2009. PMID: 18625565 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Fiducial marker guided prostate radiotherapy: a review.Br J Radiol. 2016 Dec;89(1068):20160296. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20160296. Epub 2016 Sep 23. Br J Radiol. 2016. PMID: 27585736 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modeling of Acute Rectal Toxicity to Compare Two Patient Positioning Methods for Prostate Cancer Radiotherapy: Can Toxicity Modeling be Used for Quality Assurance?OMICS J Radiol. 2018;7(5):302. doi: 10.4172/2167-7964.1000302. Epub 2018 Dec 3. OMICS J Radiol. 2018. PMID: 30775161 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Ultrasound Imaging in the External Beam Radiotherapy Workflow of Prostate Cancer Patients.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Jan 24;2018:7569590. doi: 10.1155/2018/7569590. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29619375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prostate Cancer Radiation Therapy: What Do Clinicians Have to Know?Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:6829875. doi: 10.1155/2016/6829875. Epub 2016 Dec 28. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 28116302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of prostate positioning guided by three-dimensional transperineal ultrasound and cone beam CT.Strahlenther Onkol. 2017 Mar;193(3):221-228. doi: 10.1007/s00066-016-1084-7. Epub 2016 Dec 7. Strahlenther Onkol. 2017. PMID: 27928626 Clinical Trial. English.
References
-
- International Commission on Radiation Units (ICRU) . Prescribing, recording, and reporting photon beam therapy. ICRU Report 50. Bethesda, MD: ICRU;1993.
-
- International Commission on Radiation Units (ICRU) . Prescribing, recording, and reporting photon beam therapy (Supplement to ICRU Report 50). ICRU Report 62. Bethesda, MD: ICRU; 1999.
-
- Balter JM, Lam KL, Sandler HM, Littles JF, Bree RL, Ten Haken RK. Automated localization of the prostate at the time of treatment using implanted radiopaque markers: technical feasibility. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995;33(5):1281–86. - PubMed
-
- van Herk M, Bruce A, Kroes AP, Shouman T, Touw A, Lebesque JV. Quantification of organ motion during conformal radiotherapy of the prostate by three dimensional image registration. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995;33(5):1311–20. - PubMed
-
- Crook JM, Raymond Y, Salhani D, Yang H, Esche B. Prostate motion during standard radiotherapy as assessed by fiducial markers. Radiother Oncol. 1995;37(1):35–42. - PubMed

