Percentage depth dose evaluation in heterogeneous media using thermoluminescent dosimetry
- PMID: 20160687
- PMCID: PMC5719771
- DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v11i1.2947
Percentage depth dose evaluation in heterogeneous media using thermoluminescent dosimetry
Abstract
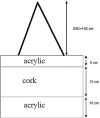
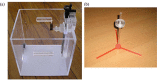
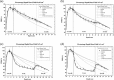
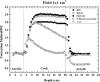
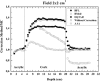
The purpose of this study is to investigate the influence of lung heterogeneity inside a soft tissue phantom on percentage depth dose (PDD). PDD curves were obtained experimentally using LiF:Mg,Ti (TLD-100) thermoluminescent detectors and applying Eclipse treatment planning system algorithms Batho, modified Batho (M-Batho or BMod), equivalent TAR (E-TAR or EQTAR), and anisotropic analytical algorithm (AAA) for a 15 MV photon beam and field sizes of 1 x 1, 2 x 2, 5 x 5, and 10 x 10 cm 2 . Monte Carlo simulations were performed using the DOSRZnrc user code of EGSnrc. The experimental results agree with Monte Carlo simulations for all irradiation field sizes. Comparisons with Monte Carlo calculations show that the AAA algorithm provides the best simulations of PDD curves for all field sizes investigated. However, even this algorithm cannot accurately predict PDD values in the lung for field sizes of 1 x 1 and 2 x 2 cm 2 . An overdosage in the lung of about 40% and 20% is calculated by the AAA algorithm close to the interface soft tissue/lung for 1 x 1 and 2 x 2 cm 2 field sizes, respectively. It was demonstrated that differences of 100% between Monte Carlo results and the algorithms Batho, modified Batho, and equivalent TAR responses may exist inside the lung region for the 1 x 1 cm 2 field.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of dose calculation algorithms in phantoms with lung equivalent heterogeneities under conditions of lateral electronic disequilibrium.Med Phys. 2004 Oct;31(10):2899-911. doi: 10.1118/1.1788932. Med Phys. 2004. PMID: 15543799
-
Monte carlo simulation of bony heterogeneity effects on dose profile for small irradiation field in radiotherapy.PLoS One. 2010 May 3;5(5):e10466. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010466. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20454675 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of dose calculation algorithms in slab phantoms with cortical bone equivalent heterogeneities.Med Phys. 2007 Aug;34(8):3323-33. doi: 10.1118/1.2750972. Med Phys. 2007. PMID: 17879796
-
High-density dental implants and radiotherapy planning: evaluation of effects on dose distribution using pencil beam convolution algorithm and Monte Carlo method.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2015 Sep 8;16(5):46–52. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v16i5.5612. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2015. PMID: 26699323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the effect of field sizes on radiation dose in the presence of metal materials using Monte Carlo simulation.Appl Radiat Isot. 2022 Apr;182:110143. doi: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2022.110143. Epub 2022 Feb 8. Appl Radiat Isot. 2022. PMID: 35152162 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a Geant4-based independent patient dose validation system with an elaborate multileaf collimator simulation model.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2019 Feb;20(2):94-106. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12530. Epub 2019 Jan 23. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2019. PMID: 30672648 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric evaluation of Acuros XB Advanced Dose Calculation algorithm in heterogeneous media.Radiat Oncol. 2011 Jul 19;6:82. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-6-82. Radiat Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21771317 Free PMC article.
-
Does dose calculation algorithm affect the dosimetric accuracy of synthetic CT for MR-only radiotherapy planning in brain tumors?J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2025 May;26(5):e70030. doi: 10.1002/acm2.70030. Epub 2025 Feb 19. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 39969229 Free PMC article.
-
Four-dimensional dosimetry validation and study in lung radiotherapy using deformable image registration and Monte Carlo techniques.Radiat Oncol. 2010 May 29;5:45. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-5-45. Radiat Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20509955 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric Analysis of Rhizophora-based Phantom Material in Radiation Therapy Applications Using Monte Carlo GATE Simulation.J Med Phys. 2023 Oct-Dec;48(4):358-364. doi: 10.4103/jmp.jmp_75_23. Epub 2023 Dec 5. J Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 38223797 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carrasco P, Jornet N, Duch M A, et al. Comparison of dose calculation algorithms in phantoms with lung equivalent heterogeneities under conditions of lateral electronic disequilibrium. Med Phys. 2004;31(10):2899–11. - PubMed
-
- Duch MA, Carrasco P, Ginjaume M., Jornet N, Ortega X, Ribas M. Dose evaluation in lung‐equivalent media in high‐energy photon external radiotherapy. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2006;120(1‐4):43–47. - PubMed
-
- Ezzell GA, Galvin JM, Low D, et al. Guidance document on delivery, treatment planning, and clinical implementation of IMRT: report of the IMRT Subcommittee of AAPM Radiation Therapy Committee. Med Phys. 2003;30(8):2089–115. - PubMed
-
- Moskvin V, Timmerman R, DesRosiers C, et al. Monte Carlo simulation of the Leksell Gamma Knife: II. Effects of heterogeneous versus homogeneous media for stereotactic radiosurgery. Phys Med Biol. 2004;49(21):4879–95. - PubMed
-
- Rosu M, Chetty IJ, Tatro DS, TenHaken RK. The impact of breathing motion versus heterogeneity effects in lung treatment planning. Med Phys. 2007;34(4):1462–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

