Novel approaches to imaging epilepsy by MRI
- PMID: 20161076
- PMCID: PMC2743439
- DOI: 10.2217/fnl.09.12
Novel approaches to imaging epilepsy by MRI
Abstract
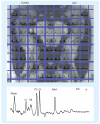
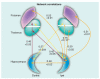
As the concept of a network of injury has emerged in the treatment of epilepsy, the importance of evaluating that network noninvasively has also grown. Recently, studies utilizing magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging, manganese-enhanced MRI and functional (f)MRI measures of resting state connectivity have demonstrated their ability to detect injury and dysfunction in cerebral networks involved in the propagation of seizures. The ability to noninvasively detect neuronal injury and dysfunction throughout cerebral networks should improve surgical planning, provide guidance for placement of devices that target network propagation and provide insights into the mechanisms of recurrence following resective surgery.
Figures


References
-
- Margerison JH, Corsellis JAN. Epilepsy and the temporal lobes. Brain. 1968;91:499–531. - PubMed
-
- Blumenfeld H, McNally KA, Vanderhill SD, et al. Positive and negative network correlations in temporal lobe epilepsy. Cereb. Cortex. 2004;14(8):892–902. - PubMed
-
- Labate A, Cerasa A, Gambardella A, Aguglia U, Quattrone A. Hippocampal and thalamic atrophy in mild temporal lobe epilepsy: a VBM study. Neurology. 2008;71(14):1094–1101. - PubMed
-
- Riederer F, Lanzenberger R, Kaya M, et al. Network atrophy in temporal lobe epilepsy: a voxel-based morphometry study. Neurology. 2008;71(6):419–425. - PubMed
-
- Gong G, Concha L, Beaulieu C, Gross DW. Thalamic diffusion and volumetry in temporal lobe epilepsy with and without mesial temporal sclerosis. Epilepsy Res. 2008;80(2–3):184–193. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
