Impact of Absorption and Transport on Intelligent Therapeutics and Nano-scale Delivery of Protein Therapeutic Agents
- PMID: 20161384
- PMCID: PMC2782827
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ces.2009.04.050
Impact of Absorption and Transport on Intelligent Therapeutics and Nano-scale Delivery of Protein Therapeutic Agents
Abstract
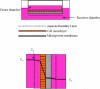
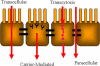
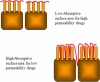
The combination of materials design and advances in nanotechnology has led to the development of new therapeutic protein delivery systems. The pulmonary, nasal, buccal and other routes have been investigated as delivery options for protein therapy, but none result in improved patient compliances and patient quality of life as the oral route. For the oral administration of these new systems, an understanding of protein transport is essential because of the dynamic nature of the gastrointestinal tract and the barriers to transport that exist.Models have been developed to describe the transport between the gastrointestinal lumen and the bloodstream, and laboratory techniques like cell culture provide a means to investigate the absorption and transport of many therapeutic agents. Biomaterials, including stimuli-sensitive complexation hydrogels, have been investigated as promising carriers for oral delivery. However, the need to develop models that accurately predict protein blood concentration as a function of the material structure and properties still exists.
Figures

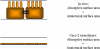
References
-
- Ahsan F, Arnold J, Meezan E, Pillion DJ. Enhanced bioavailability of calcitonin formulated with alkylglycosides following nasal and ocular administration in rats. Pharmaceutical Research. 2001;18(12):1742–1746. - PubMed
-
- Amin A, Shah T, Patel J, Gajjar A. Non-invasive Insulin Delivery Technologies: Current Trends & Future Prospects. Drug Delivery Technology. 2006;6(3):48–60.
-
- Amin A, Shah T, Patel J, Gajjar A. Non-invasive Insulin. Drug Delivery Technology. 2008;8(3):43–48.
-
- Arora P, Sharma S, Garg S. Permeability issues in nasal drug delivery. Drug Discovery Today. 2002;7(18):967–975. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
