Biomedical applications of chemically-modified silk fibroin
- PMID: 20161439
- PMCID: PMC2790051
- DOI: 10.1039/b905802h
Biomedical applications of chemically-modified silk fibroin
Abstract
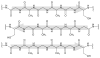
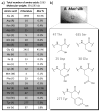
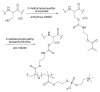
Silk proteins belong to a class of unique, high molecular weight, block copolymer-like proteins that have found widespread use in biomaterials and regenerative medicine. The useful features of these proteins, including self-assembly, robust mechanical properties, biocompatibility and biodegradability can be enhanced through a variety of chemical modifications. These modifications provide chemical handles for the attachment of growth factors, cell binding domains and other polymers to silk, expanding the range of cell and tissue engineering applications attainable. This review focuses on the chemical reactions that have been used to modify the amino acids in silk proteins, and describes their utility in biomedical applications.
Figures
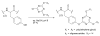
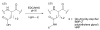
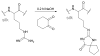
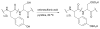
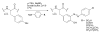
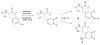
References
-
- Zhou CZ, Confalonieri F, Jacquet M, Perasso R, Li ZG, Janin J. Proteins. 2001;44:119–122. - PubMed
-
- Heslot H. Biochimie. 1998;80:19–31. - PubMed
-
- Horan RL, Antle K, Collette AL, Wang Y, Huang J, Moreau JE, Volloch V, Kaplan DL, Altman GH. Biomaterials. 2005;26:3385–3393. - PubMed
-
- Wang X, Wenk E, Matsumoto A, Meinel L, Li C, Kaplan DL. J Control Release. 2007;117:360–370. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
