Radioprotection in normal tissue and delayed tumor growth by blockade of CD47 signaling
- PMID: 20161613
- PMCID: PMC2811586
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3000139
Radioprotection in normal tissue and delayed tumor growth by blockade of CD47 signaling
Abstract
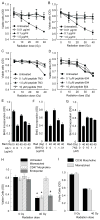
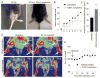
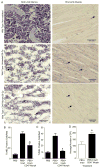
Radiation-induced damage of normal tissues restricts the therapeutic doses of ionizing radiation that can be delivered to tumors and thereby limits the effectiveness of radiotherapy. Thrombospondin-1 signaling through its cell surface receptor CD47 limits recovery from several types of stress, and mice lacking either gene are profoundly resistant to radiation injury. We describe strategies to protect normal tissues from radiation damage using CD47 or thrombospondin-1 antibodies, a CD47-binding peptide, or antisense suppression of CD47. A morpholino oligonucleotide targeting CD47 confers radioresistance to human endothelial cells in vitro and protects soft tissue, bone marrow, and tumor-associated leukocytes in irradiated mice. In contrast, CD47 suppression in mice bearing melanoma or squamous lung tumors prior to irradiation result in 89% and 71% smaller tumors, respectively. Thus, inhibiting CD47 signaling maintains the viability of normal tissues following irradiation while increasing the radiosensitivity of tumors.
Figures
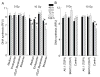


References
-
- Nair CK, Parida DK, Nomura T. Radioprotectors in radiotherapy. J Radiat Res (Tokyo) 2001;42:21–37. - PubMed
-
- Emami B, et al. Tolerance of normal tissue to therapeutic irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1991;21:109–122. - PubMed
-
- Stone HB, Coleman CN, Anscher MS, McBride WH. Effects of radiation on normal tissue: consequences and mechanisms. Lancet Oncol. 2003;4:529–536. - PubMed
-
- Duchstein S, Gademann G, Peters B. Early and late effects of local high dose radiotherapy of the brain on memory and attention. Strahlenther Onkol. 2003;179:441–451. - PubMed
-
- Coleman CN. Radiation oncology--linking technology and biology in the treatment of cancer. Acta Oncol. 2002;41:6–13. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

